Barleria.
The Plant List recognises 296 species and 186 synonyms.
Barleria are characterised by having a calyx with 4 sepals in 2 pairs plus microscopic features of
the pollen grains and leaf cystoliths.
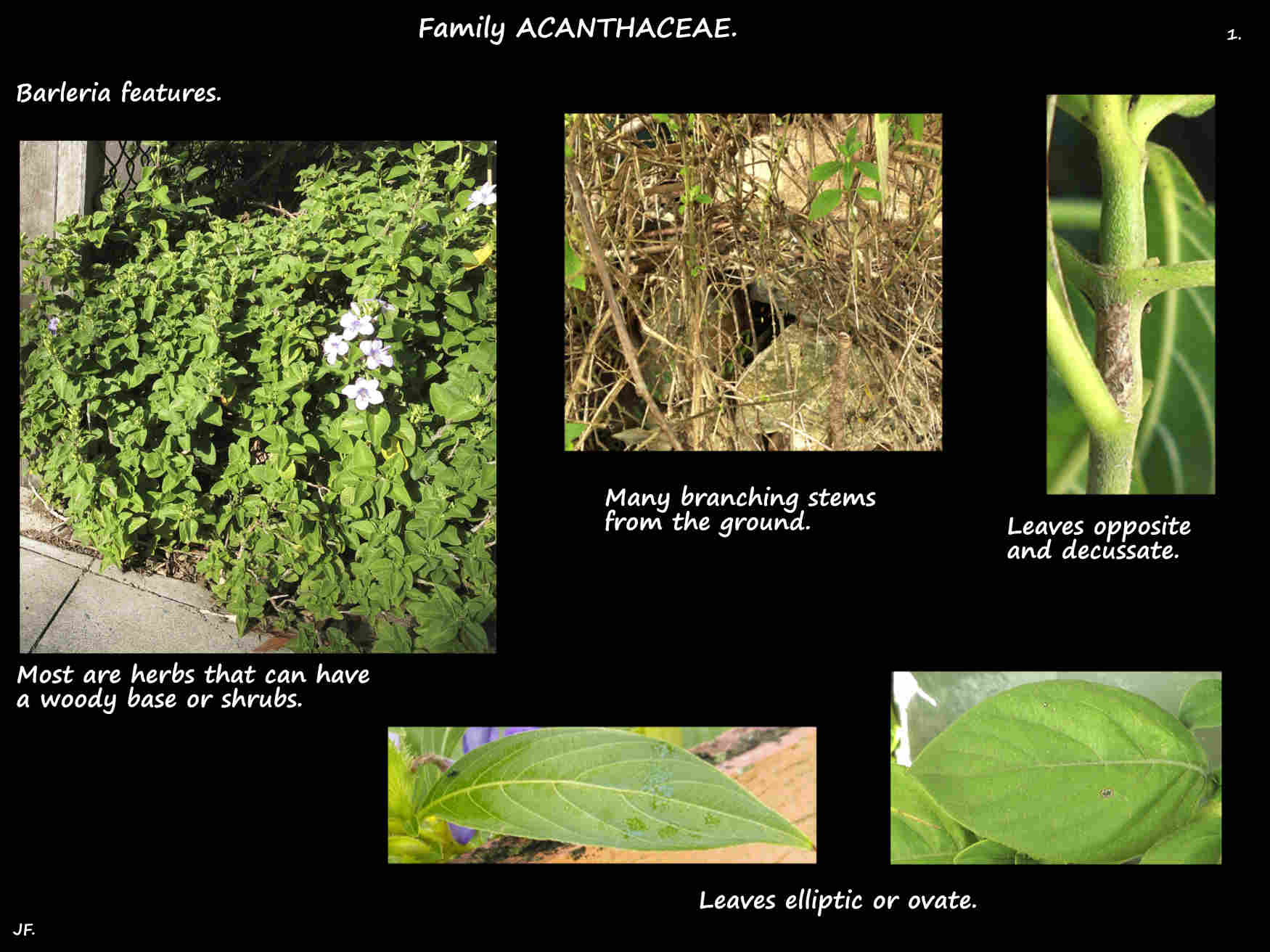
They are herbs sometimes with a woody base, shrubs that sometimes have thorns or occasionally climbers.
The stems can be angular to almost circular in cross section.
Plants can be evergreen or deciduous.
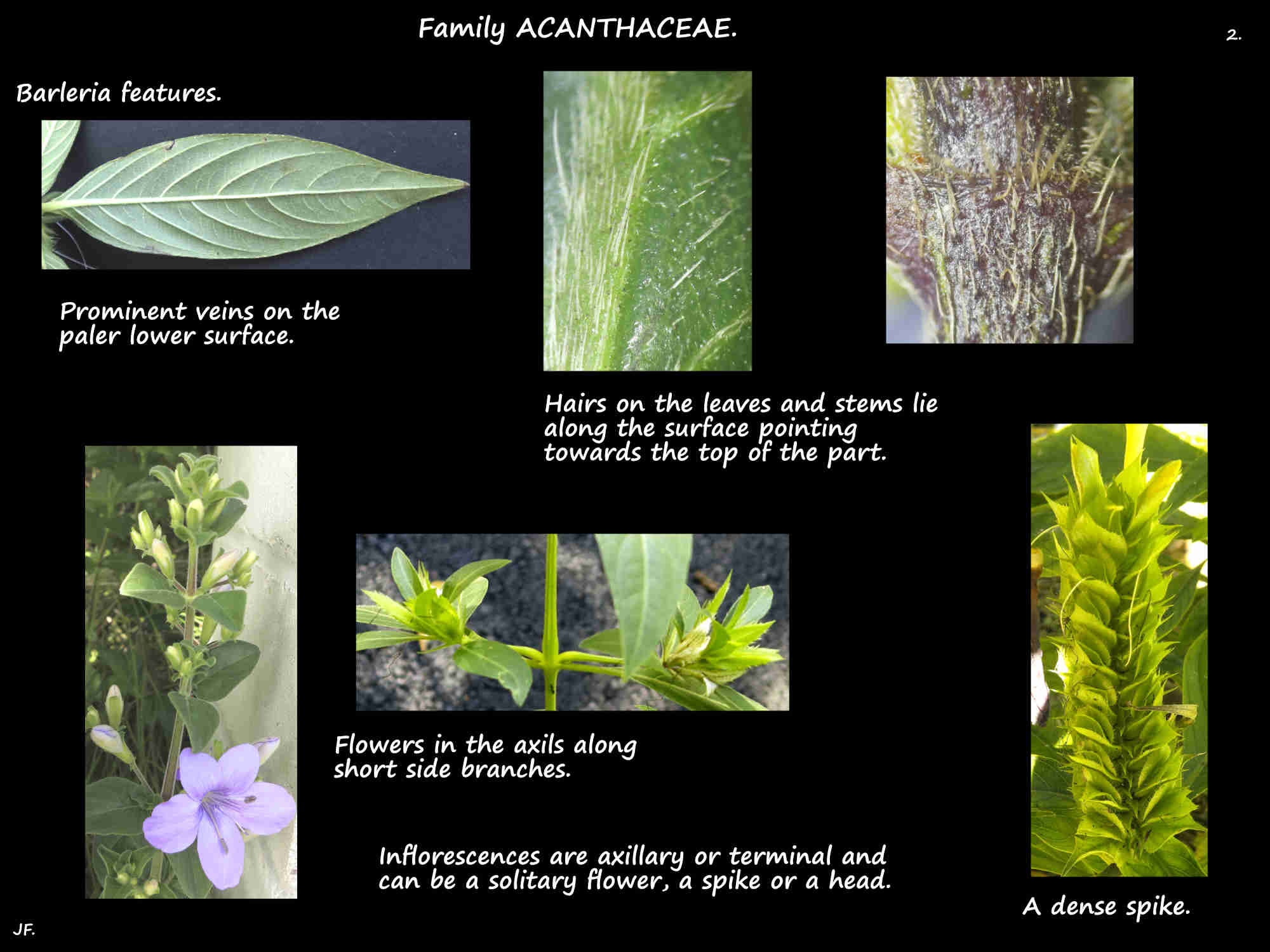
The simple leaves, with or without a petiole are opposite and decussate.
The leaves at a node may be a different shape or size.
The blade mostly has a smooth edge but is occasionally toothed or has a spine at the tip.
Some leaves are transformed into spines.
Stellate or glandular hairs may be present on the leaves and the cystoliths may be in pairs.
Inflorescences are axillary or terminal.
They can be a solitary flower, a spike or a head.
The spikes may branch forming a dense cluster.
Where there is more than 1 flower the upper ones open first (cymes).
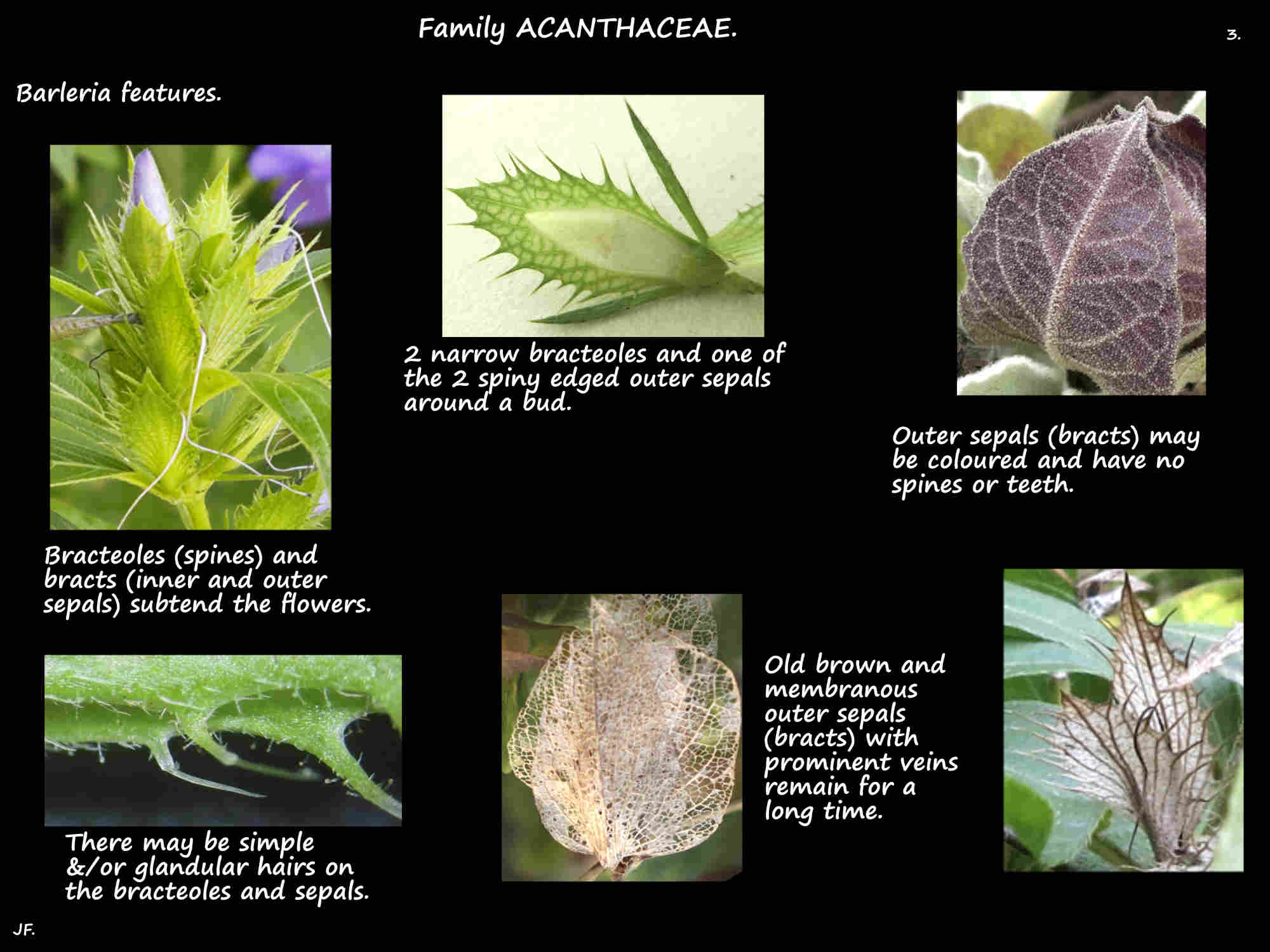
(In descriptions the terms spike, bract, bracteole and inner and outer sepals are used differently.)
Flowers are subtended by paired narrow bracteoles (spines).
They are 10 to 15 mm long and around 2 mm wide.
They can be leaf-like, membranous or leathery and the edge can be smooth, toothed, hairy or spiny.
Both may be on the same side of the stem and occasionally they are reduced to a solid spine.
The calyx has 4 sepals (bracts) in 2 whorls.
The outer pair are much larger and sometimes one is longer than the other.
They are broadly ovate to linear-lanceolate and often leaf-like.
The inner pair of sepals are shorter and narrower.
All can have a smooth or toothed edge with a spine at the tip and simple and glandular hairs.
Sometimes the smaller one has a bifid or rounded tip.
Flowers, with or without a pedicel are up to 12 cm long.
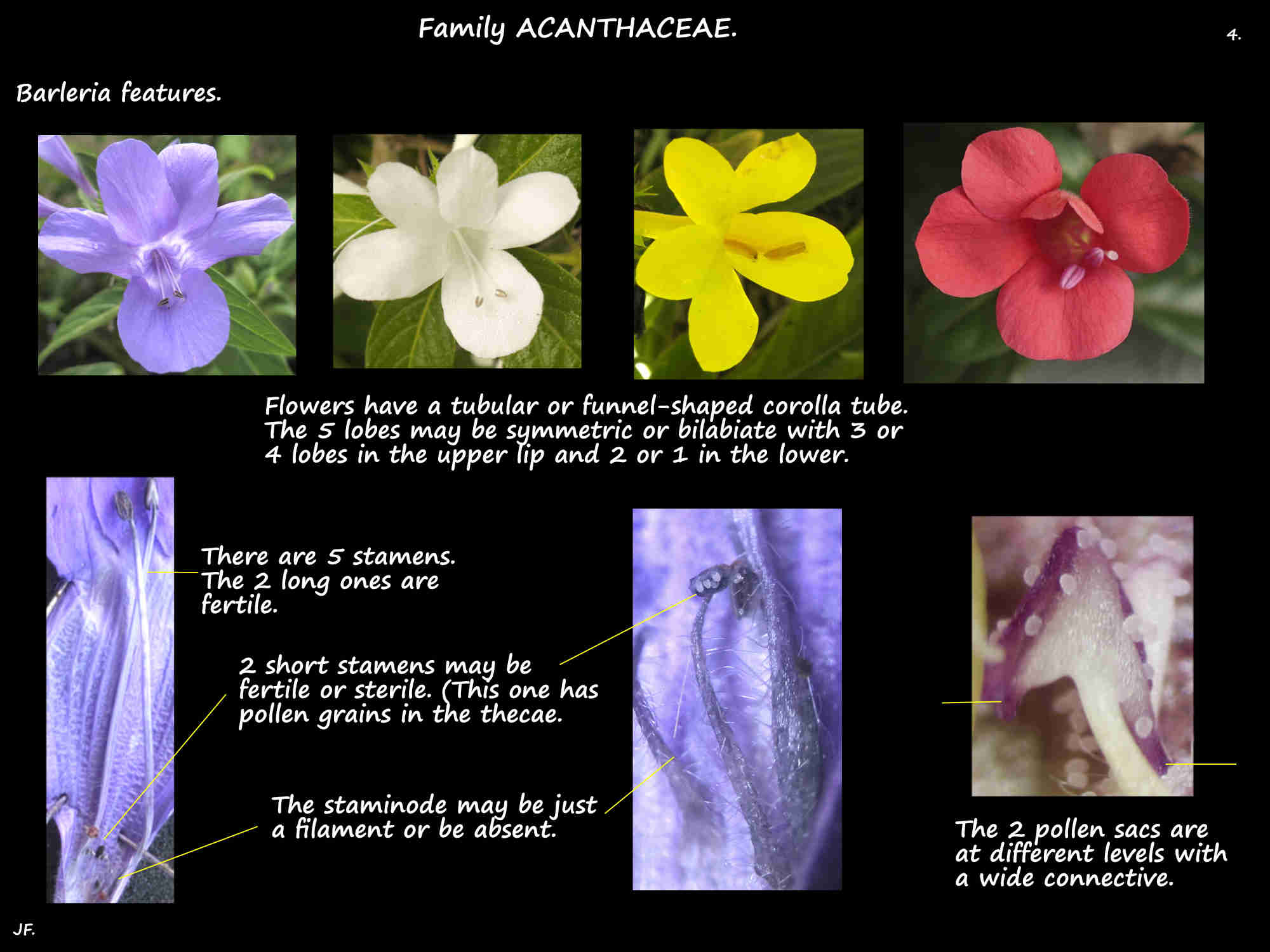
They vary from almost radially symmetric to markedly 2-lipped.
There are 5 lobes but occasionally the lower 2 are fused.
Below the insertion of the stamens the corolla tube is usually a narrow cylinder.
Above this it can be tubular, funnel or bell-shaped.
Bilabiate corollas can have 3 or 4 lobes in the upper lip with 2 or 1 in the lower lip respectively.
The lower obovate lobe may have a slightly notched tip.
They come in mauve, purple, blue, red, yellow, orange as well as white.
Some have coloured blotches on them.
There are typically 5 stamens with 2 long fertile ones and 2 short ones plus a staminode.
They insert into the corolla tube in line with the base of the petal lobes.
The filaments have hairs at the base.
The 2 longer stamens twist through 180 degrees near the base then cross over.
Their anthers have 2 parallel blunt lobes or thecae that open through long slits.
The 2 smaller stamens have anthers but these usually produce no pollen.
The central staminode is even smaller and may or may not have an anther.
The staminode may be absent.
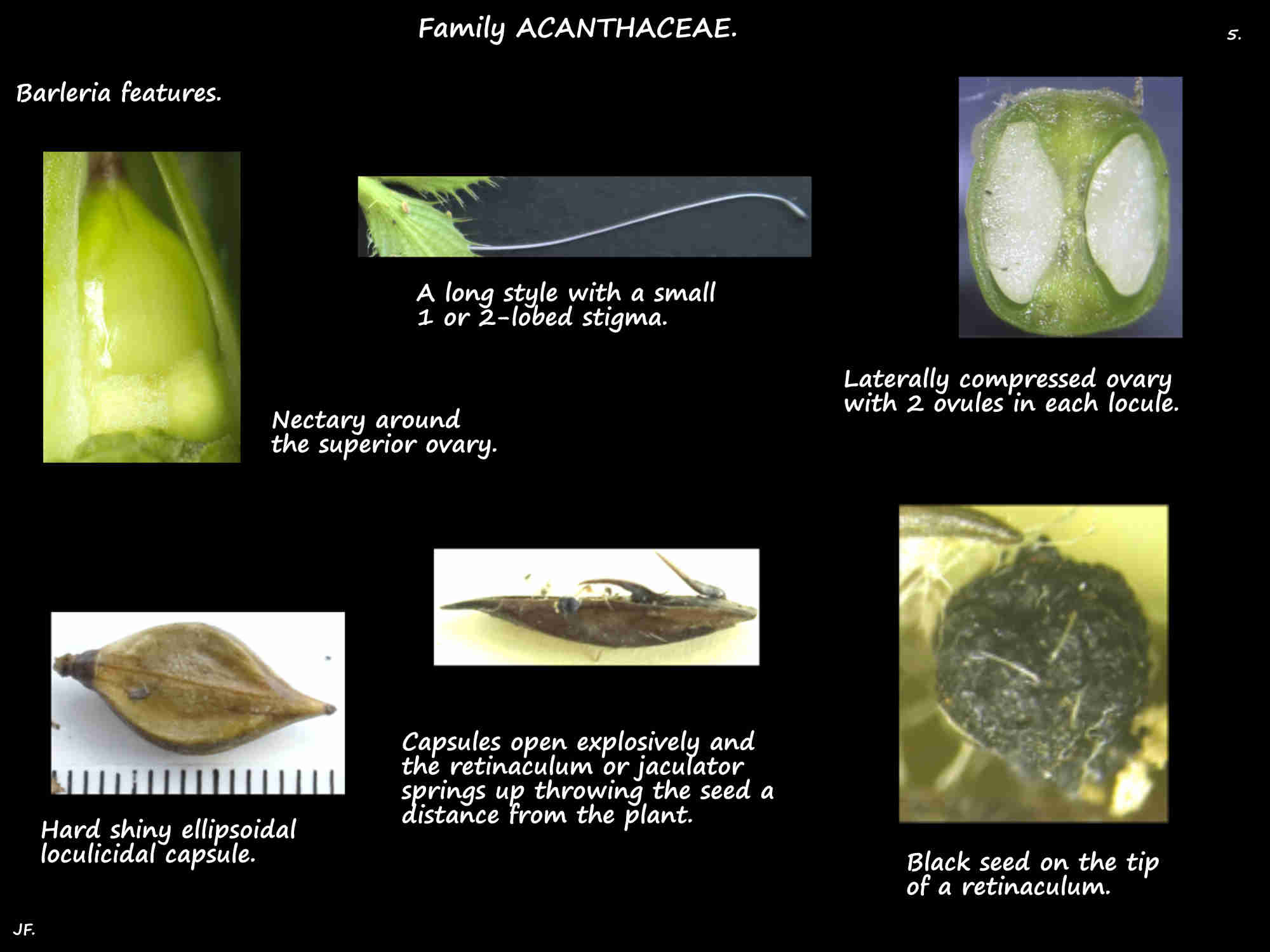
There is a cup-like nectary around the base of the ovary.
The superior ovary, of 2 fused carpels has 2 locules each with 2 ovules.
The ovules are vertically arranged but usually only 1 develops in each locule.
The long slender style may have hairs on the base.
The stigma has 1 or 2 lobes.
Fruit are loculicidal capsules that may have a beak.
There are 1 to 4 usually flattened seeds with a retinaculum or jaculator.
Seeds have obvious or minute hairs.
J.F.