Combretum. (Quisqualis.)
The genus has 285 species according to Plants of the World Online (Kew).
They are native to large areas of the tropics and sub-tropics especially Africa.
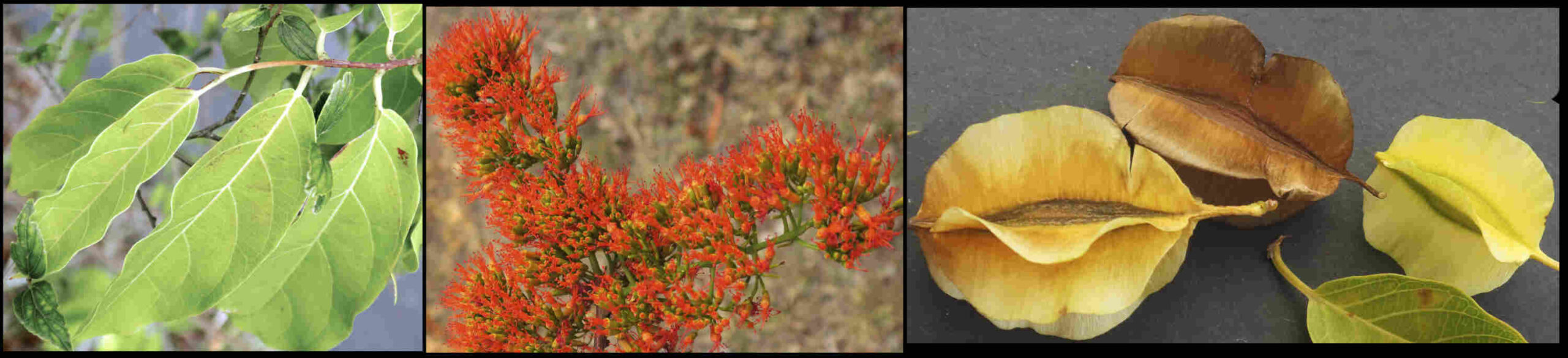
Plants are shrubs that commonly scramble or climb or lianas (woody vines).
There are a few small trees and the vines climb using twining stems.
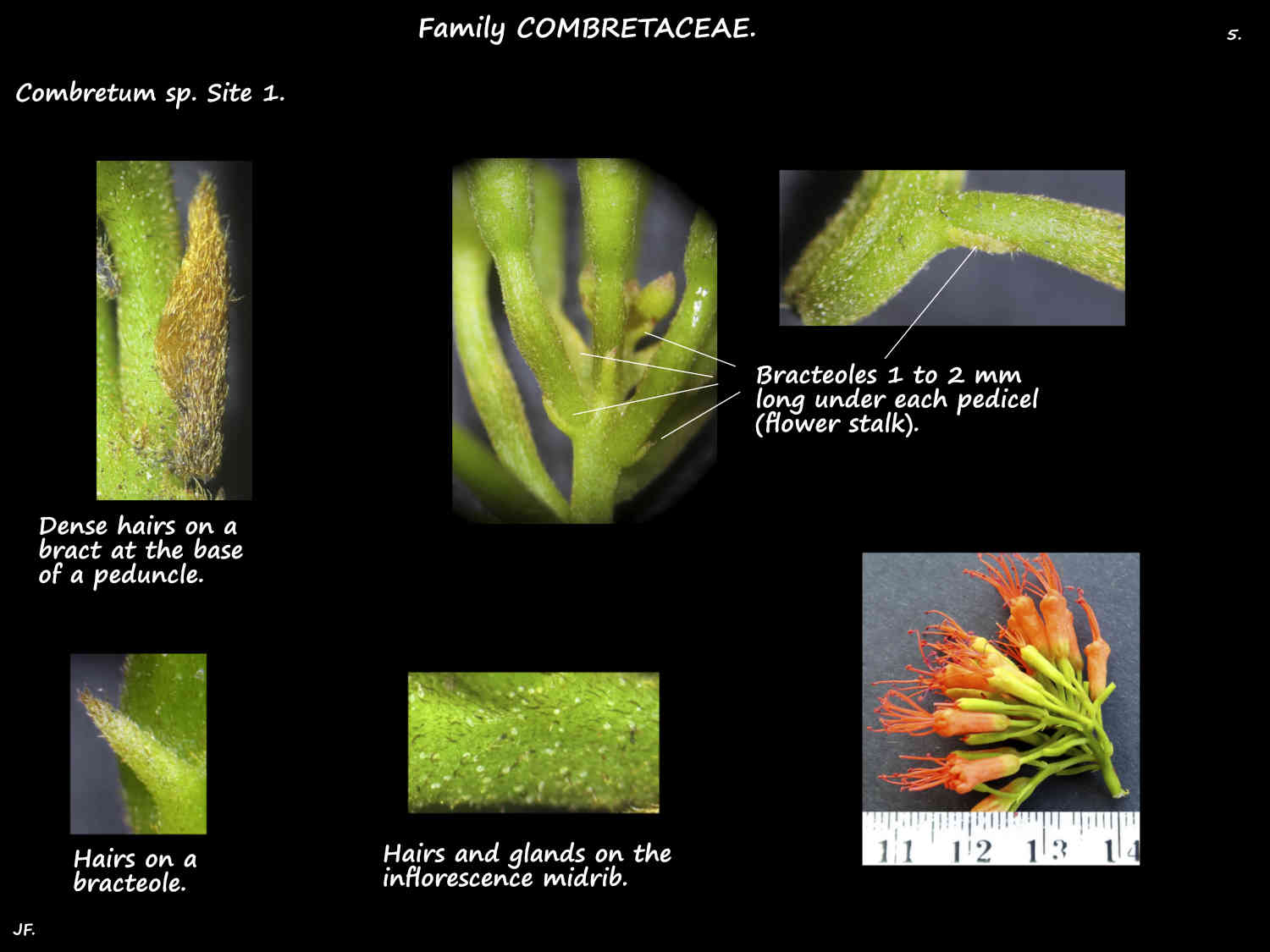
Parts have simple hairs, glands with or without a stalk and sometimes scales.
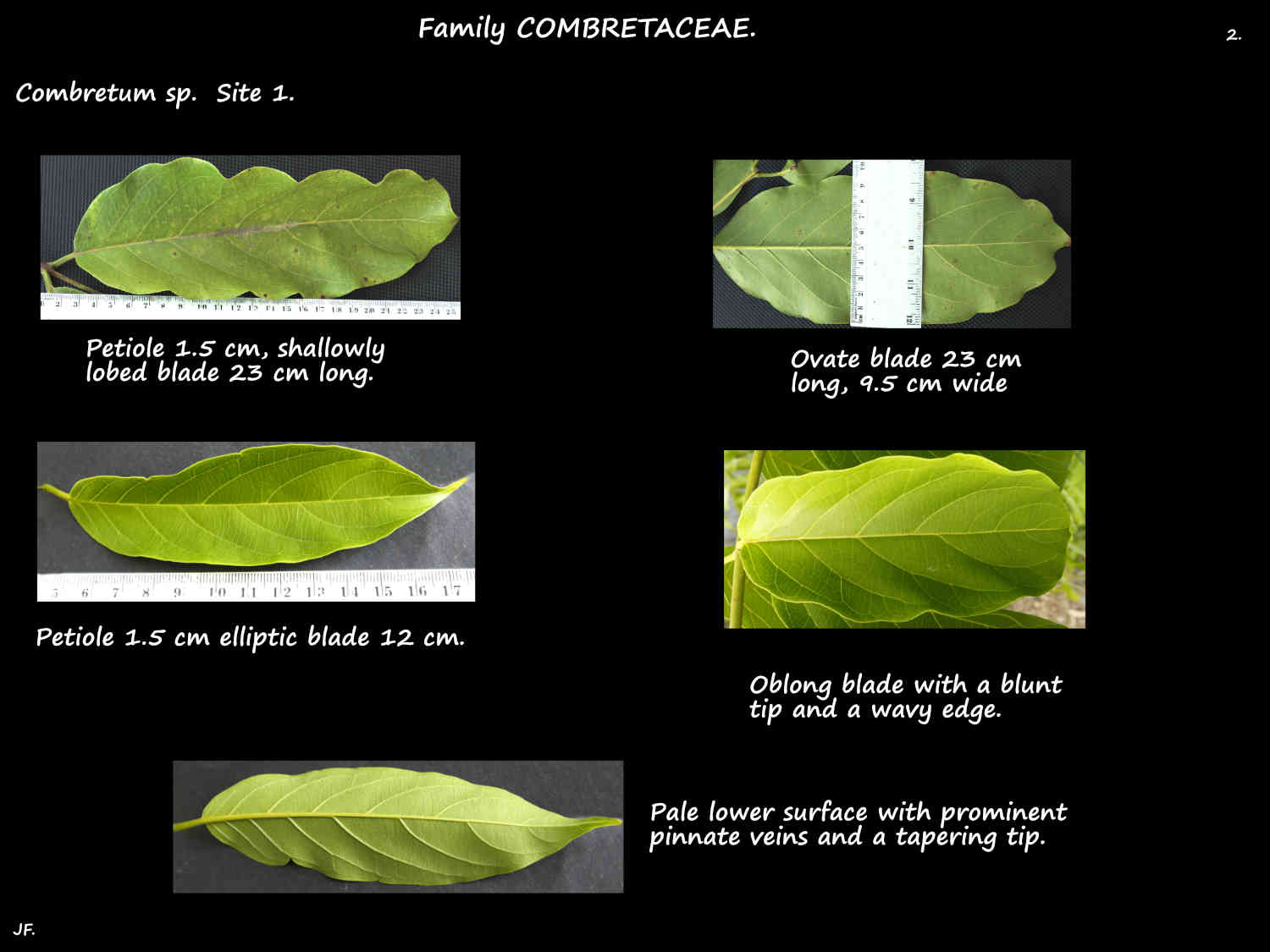
Leaves, typically on a petiole are opposite or whorled but rarely alternate.
The petioles may persist and become ‘spines’ that aid climbing.
The blades are variable in shape and can be elliptic, ovate or oblong.
There may be hairs, scales and domatia (pores).
Terminal or axillary inflorescences are racemes, spikes or occasionally panicles.
Bracts, sometimes leafy are present.
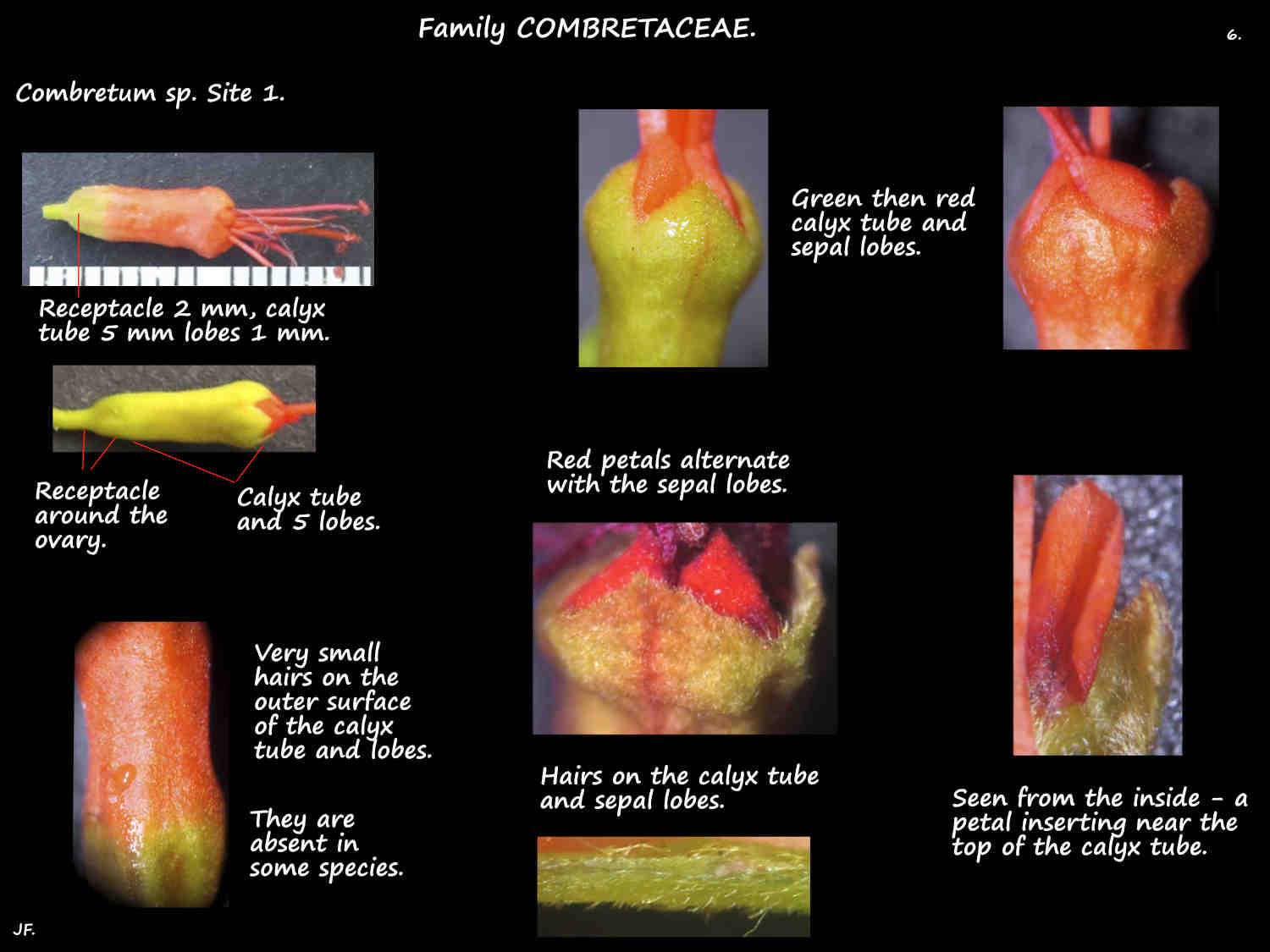
The calyx is in 2 variously named sections – the lower and upper receptacle, hypanthium or calyx tube or a mix of these.
(I will use receptacle for the lower section and calyx tube for the upper.)
The receptacle surrounds, and is fused to the ovary.
The calyx tube can be tubular or funnel-shaped.
Around 5 (2 – 9) cm long it has 4 or 5 usually small lobes on the rim.
It may have some hairs and occasionally has scales.
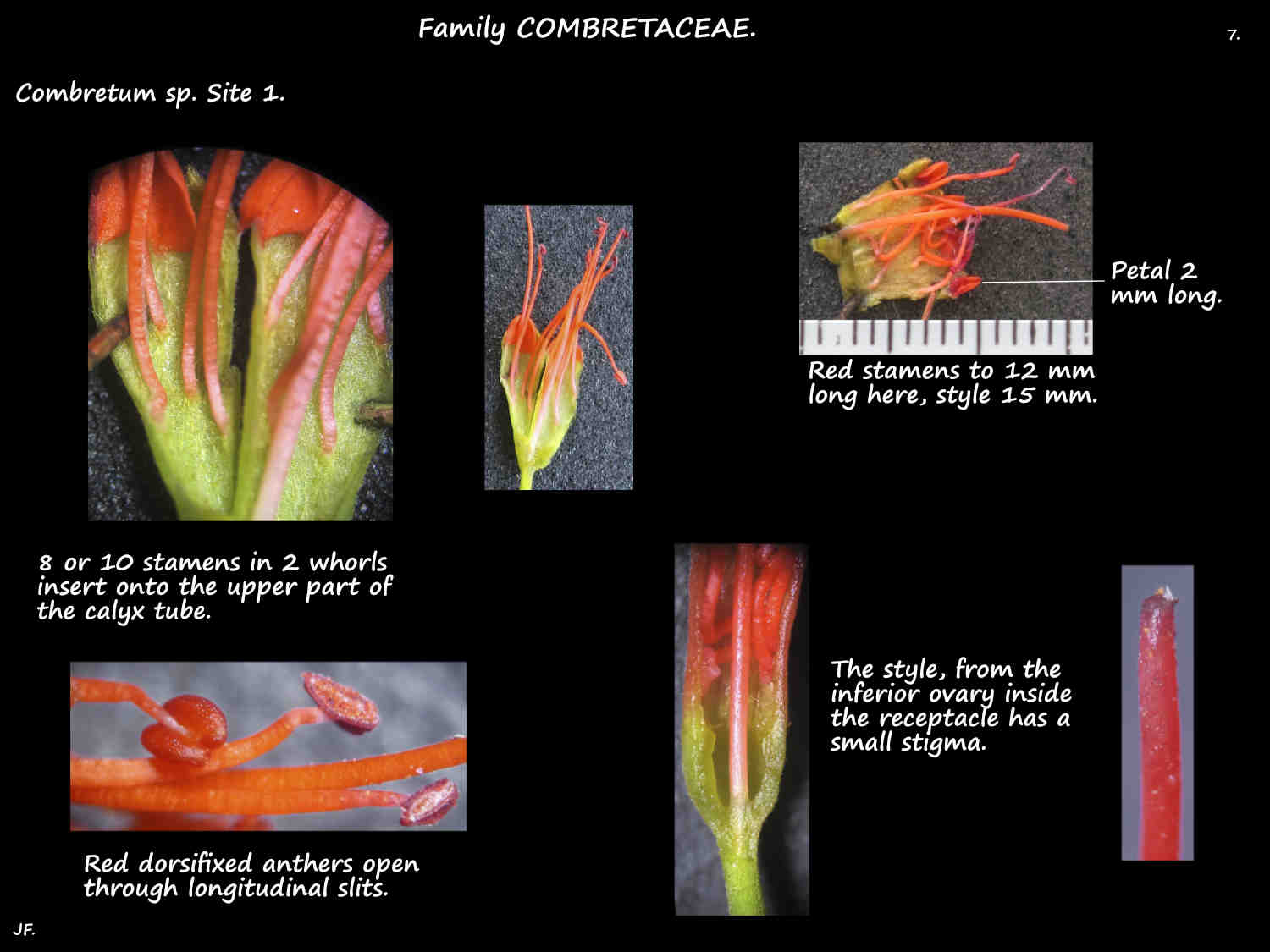
The 4 or 5 (0) petals, up to 2 cm long insert onto the calyx tube.
Petals can be white, red, yellow, orange or purple.
Typically there are 8 or 10 stamens in 2 whorls inserted near the top of the calyx tube.
The dorsifixed anthers may lie inside the tube or extend past it.
There may be a smooth or hairy nectiferous disk between the stamens and ovary.
The inferior ovary has 1 locule typically with 2 ovules of which 1 aborts.
The upper part of the style is free but the rest is fused to the calyx tube.
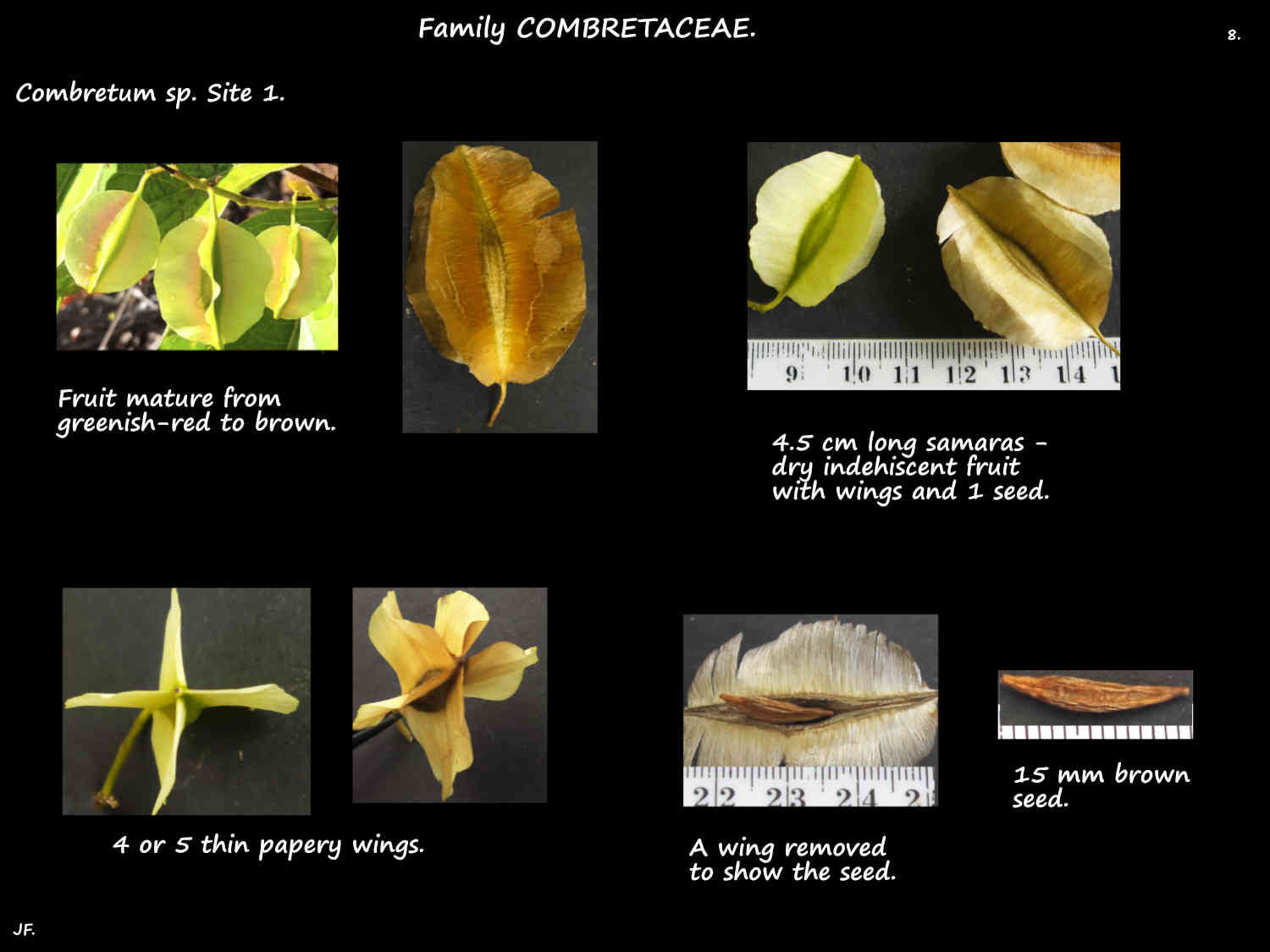
The fruit, with or without a stalk usually do not rupture or do so very late.
The ovoid, ellipsoidal or almost round fruit have 5 longitudinal ridges or wings.
J.F.