The Agaricales.
Basidiomycota > Agaricomycetes > Agaricales.
The majority of species are typical “gilled mushrooms” with a stem and a usually fleshy cap.
Under the cap are the gills where the spores are produced.
Also included are a variety of other types of fruit bodies and gilled mushrooms occur in different orders.
There are about 30-33 families, about 400 to 410 genera and over 13,000 species.
There are several genera not yet assigned to a family.
Mushroom Families that have true gills.
Common families include Agaricaceae, Amanitaceae, Bolbitiaceae, Cortinariaceae, Omphalotaceae, Psathyrellaceae, Pleurotaceae and Pluteaceae.
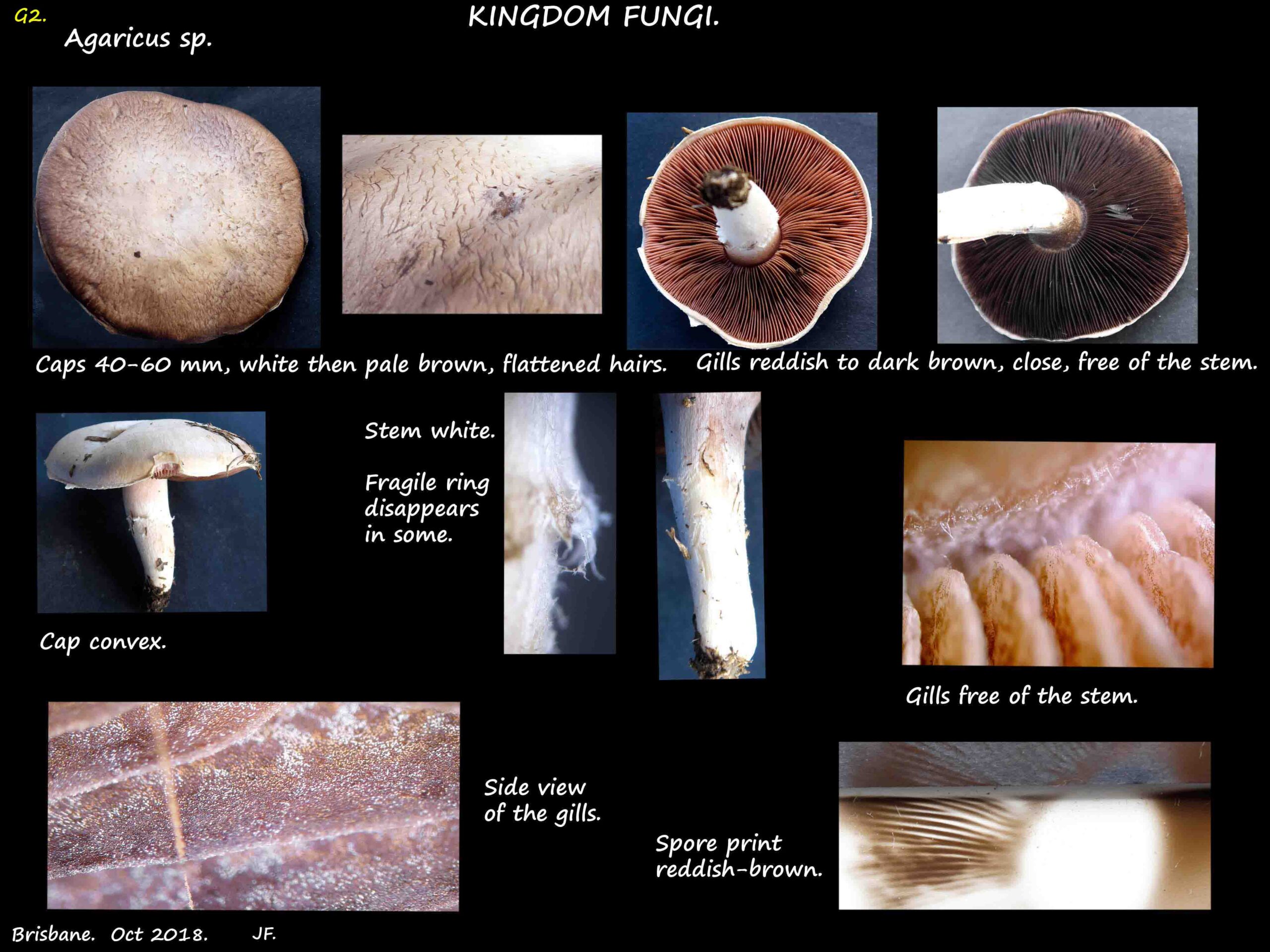
Family Agaricaceae.
Basidiomycota > Agaricomycetes > Agaricales > Agaricaceae.
It has about 85 genera and the type genus is Agaricus with about 400 species.
As well as typical gilled mushrooms it also has some puffballs and Bird’s Nest fungi.
General characteristics include –
- Usually solitary, short lasting, live on dead organic material on the ground.
- Cap 1 to 26 cm across, often white, cream or brown but also yellow or rarely green.
- Caps that are either flat, convex, parasol-like or with a central hump (umbonate).
- They may be smooth or covered in warts.
- Some bruise rapidly when damaged (turning brown, red or yellow).
- The gills under the cap are thin and not attached to the stem.
- The stem is usually attached to the centre of the cap.
- Typically there is a membrane-like partial veil between the stem and cap edge.
- There is a ring on the stem but no volva at the base (Lepiota may have ring remnants).
- The spore print may be white, sepia, pink, ochre or greenish.
- It may be brown but is never rusty-brown or cinnamon-brown.
J.F.