Solanum laxum or Solanum jasminoides.
In Family Solanaceae it is known as the Potato Vine or Jasmine Nightshade.
Having escaped from gardens it is now naturalised in Brisbane.
There are a few cultivars such as Star Light and Album and its variegated form.
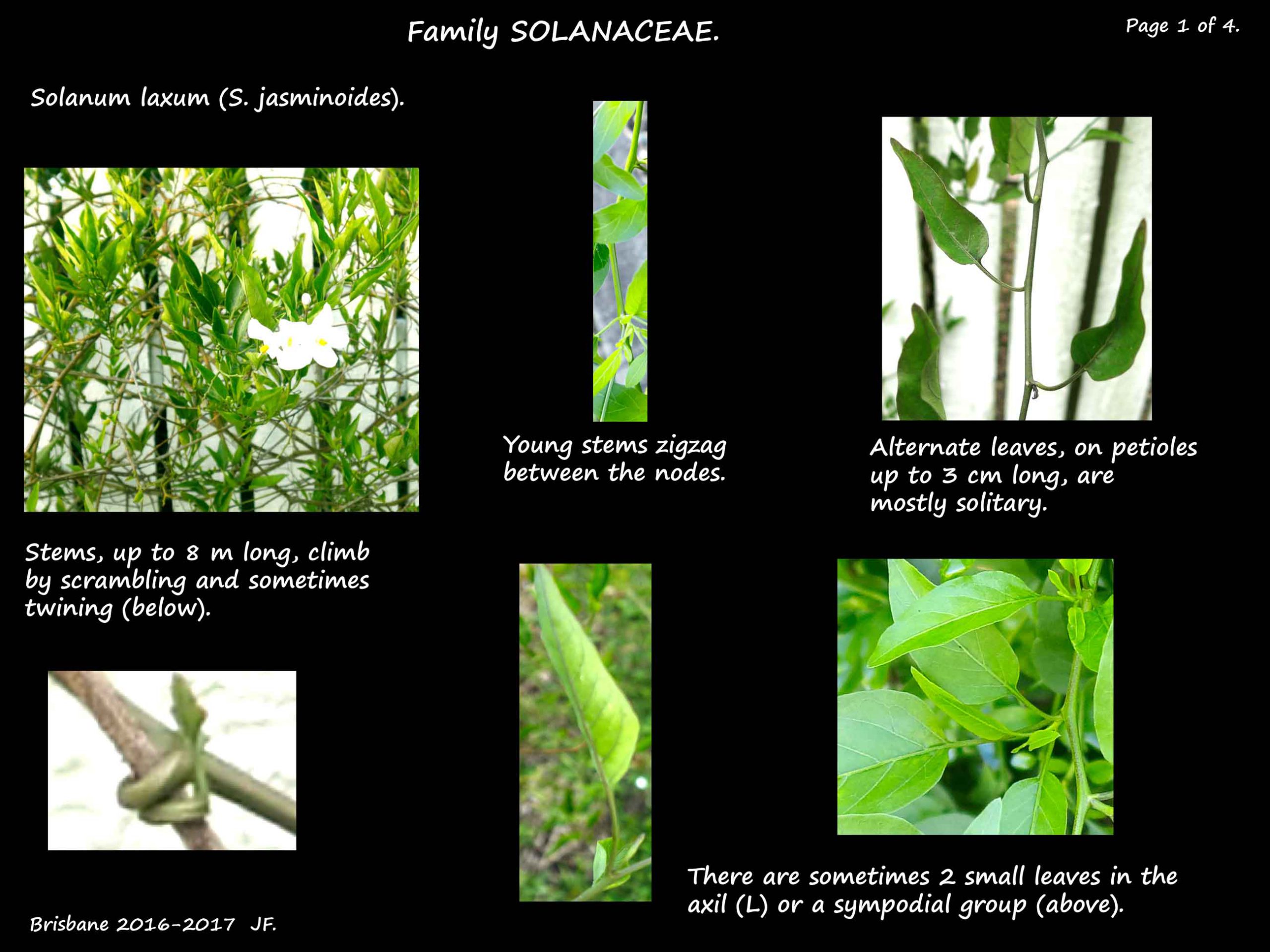
They are vines with stems up to 8 m long that climb by scrambling and twining.
Young green stems zigzag between the nodes.
They are hairless or have a few very small, simple white hairs.
Older branches are woody and may have a purplish tinge.
The alternate leaves are on petioles up to 2 or 3 cm long.
There are small tufts of simple hairs in the leaf axils.
At each node the leaf may be solitary or have 2 small leaves in the axil.
There can also be several leaves in a group known as a sympodium.
This forms when the stem stops growing and is replaced by a new lateral or axillary shoot.
Successive axillary buds repeatedly replace the growing tip.
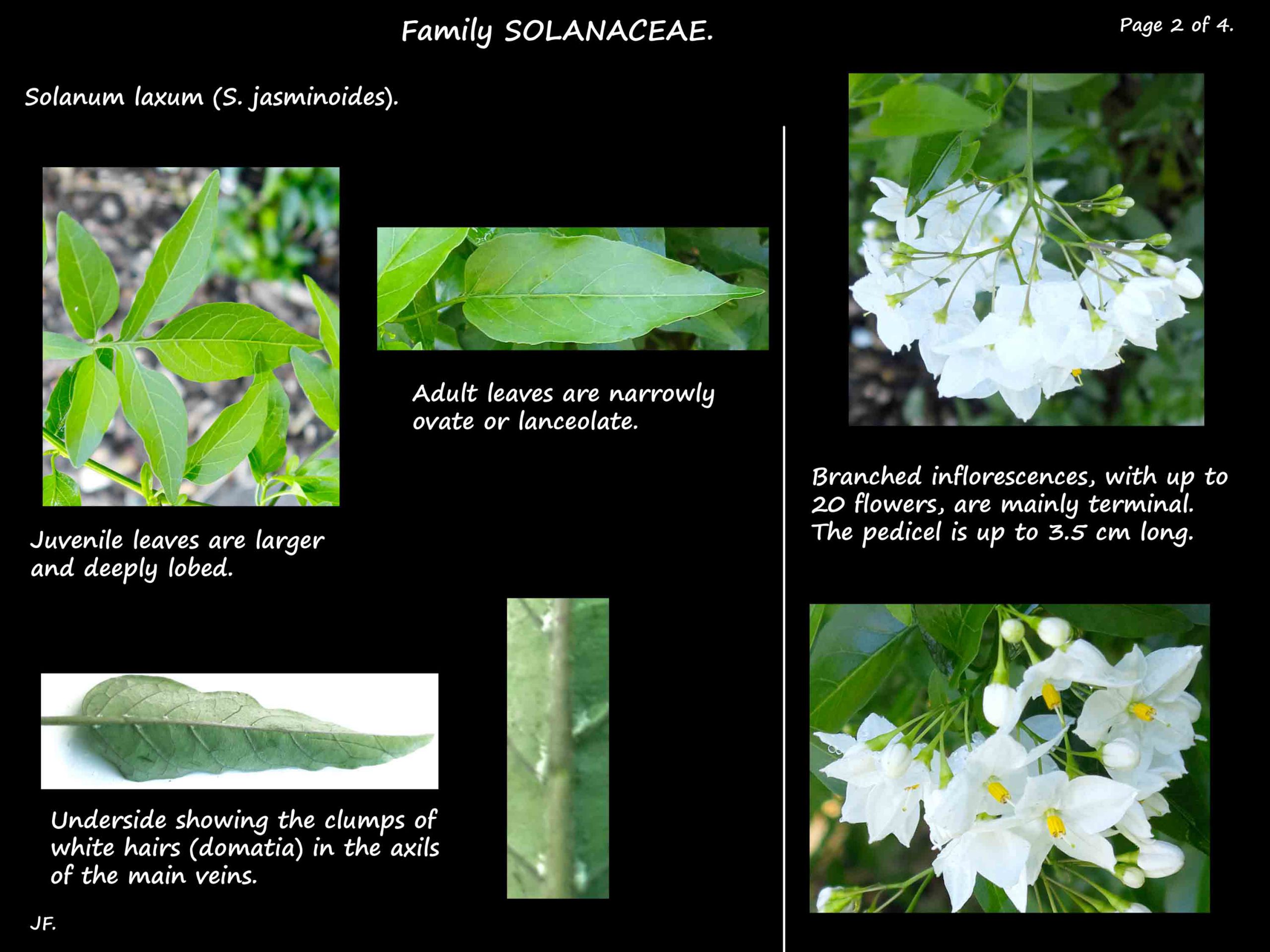
Juvenile leaves, up to 7 cm long, are larger than the adult ones and deeply lobed.
Adult leaves are narrowly ovate to lanceolate with a pointed tip.
They are mostly simple but occasional ones have a few shallow lobes.
The blade is up to 5 cm long and 2.5 cm wide.
There are small tufts of hairs (domatia) in the axils of the main veins on the lower surface.
The branched inflorescences are mainly terminal with some later being lateral.
Each can have 20 or more flowers on a stalk up to 3.5 cm long.
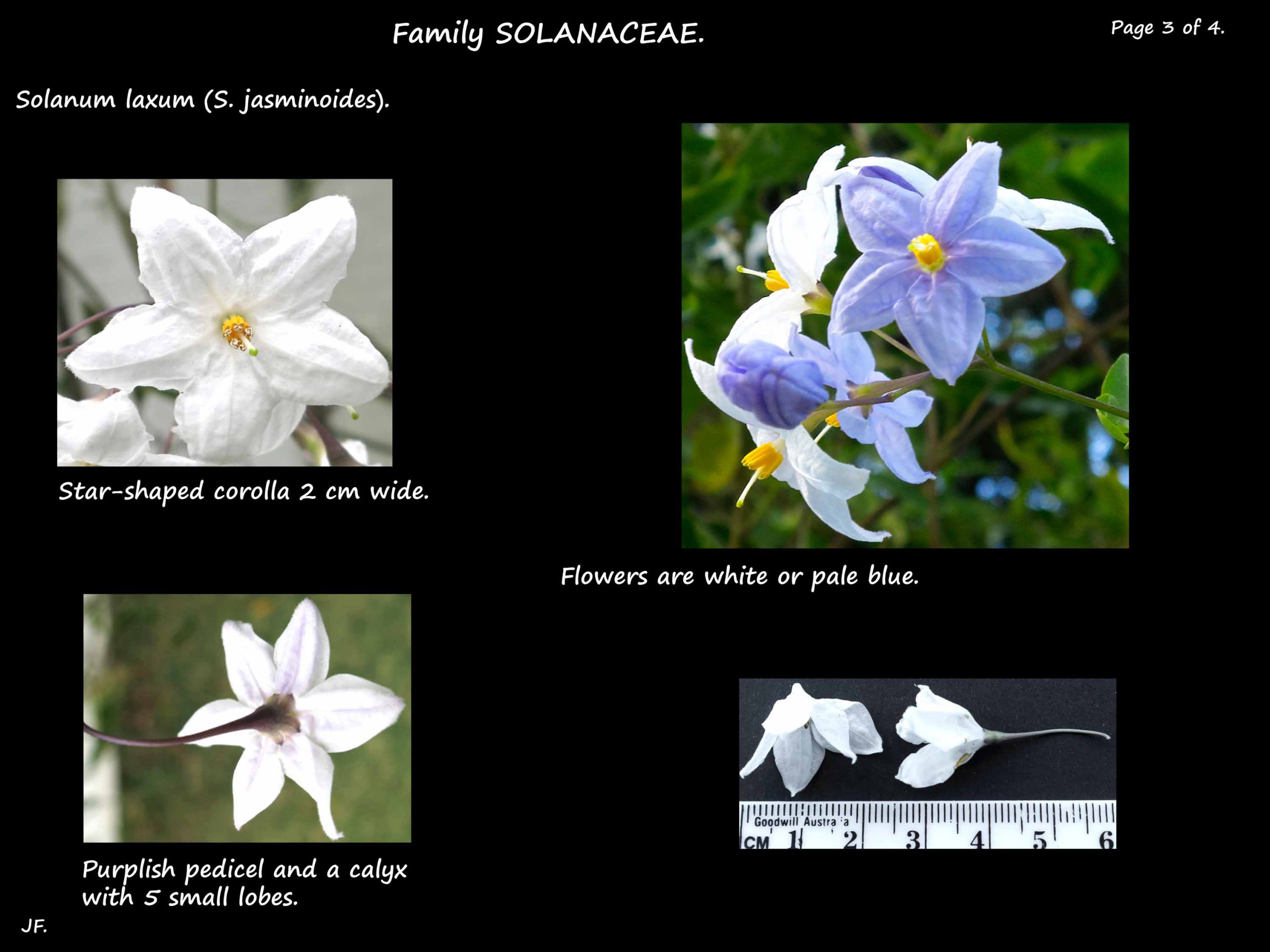
Each flower, with parts in fives, is on a 1 to 1.5 cm long, purplish stalk.
The sepal bases form a short tube with pointed lobes 1.5 mm long.
The petal bases are also fused with the flaring lobes forming a corolla 2 cm across.
The petals are white or a pale blue.
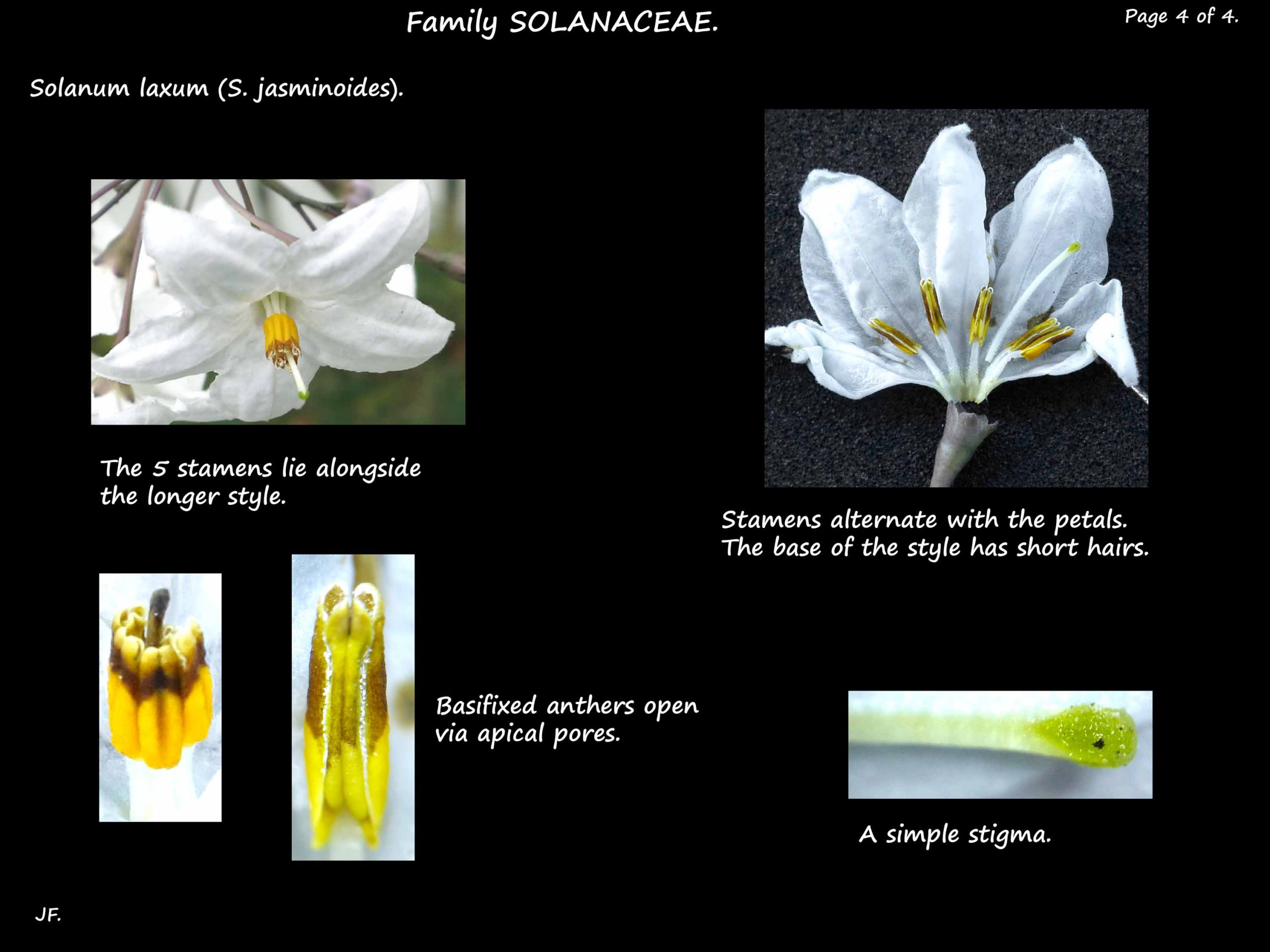
The stamens, with anthers around 3 mm long, lie alongside the style.
The bright yellow anthers open via apical pores.
The style, with a small green stigma, extends well past the anthers.
The fruit are berries around 8 mm across that ripen to a shiny bluish-black.
J.F.