Solanum mauritianum.
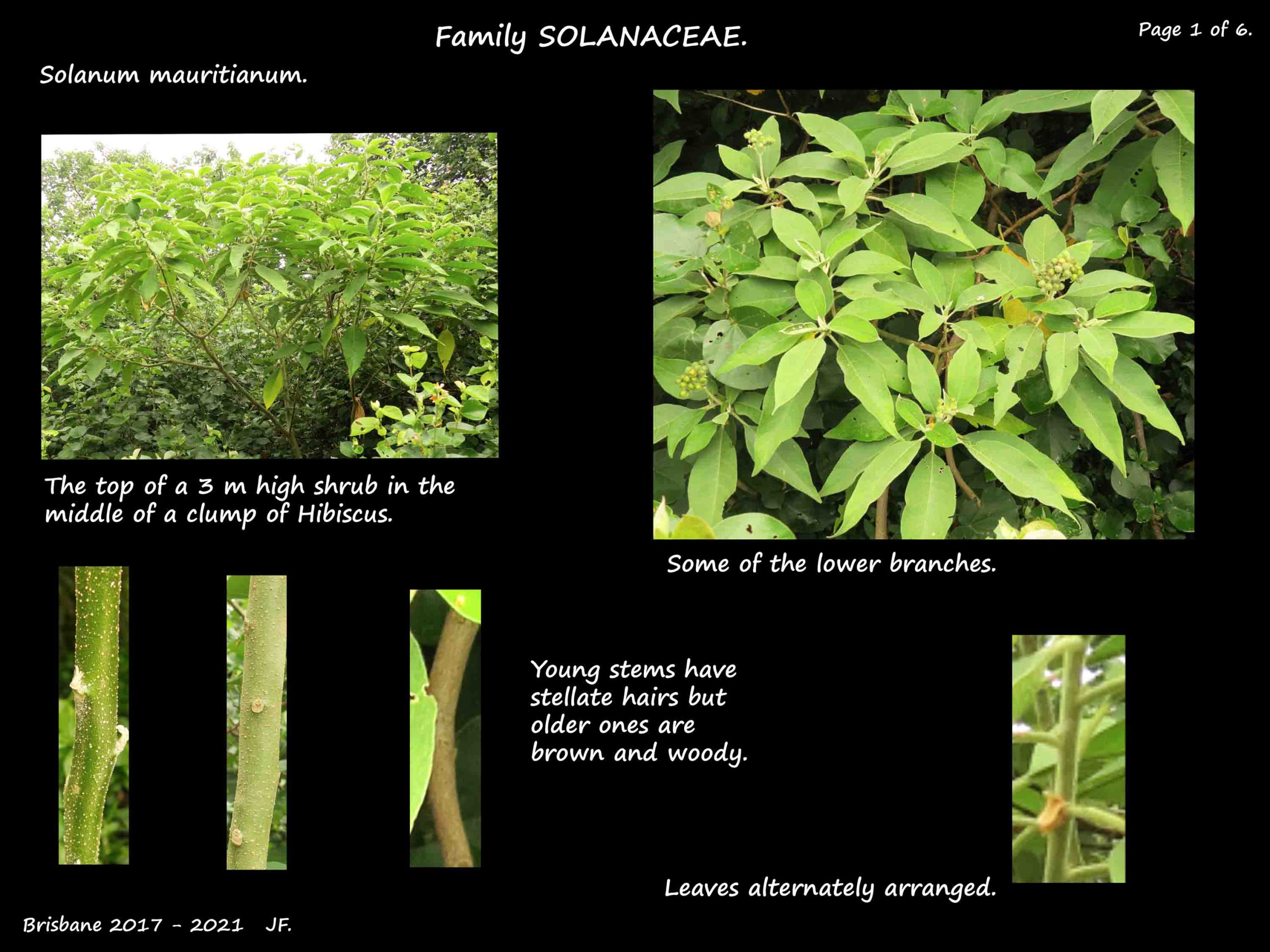
Wild Tobacco, native to South America, is naturalised in Queensland where it is a weed.
They are fast growing, long lived shrubs or trees 2 to 4 m high but occasionally up to 10 m.
Stems are covered in dense stellate hairs but there are no prickles.
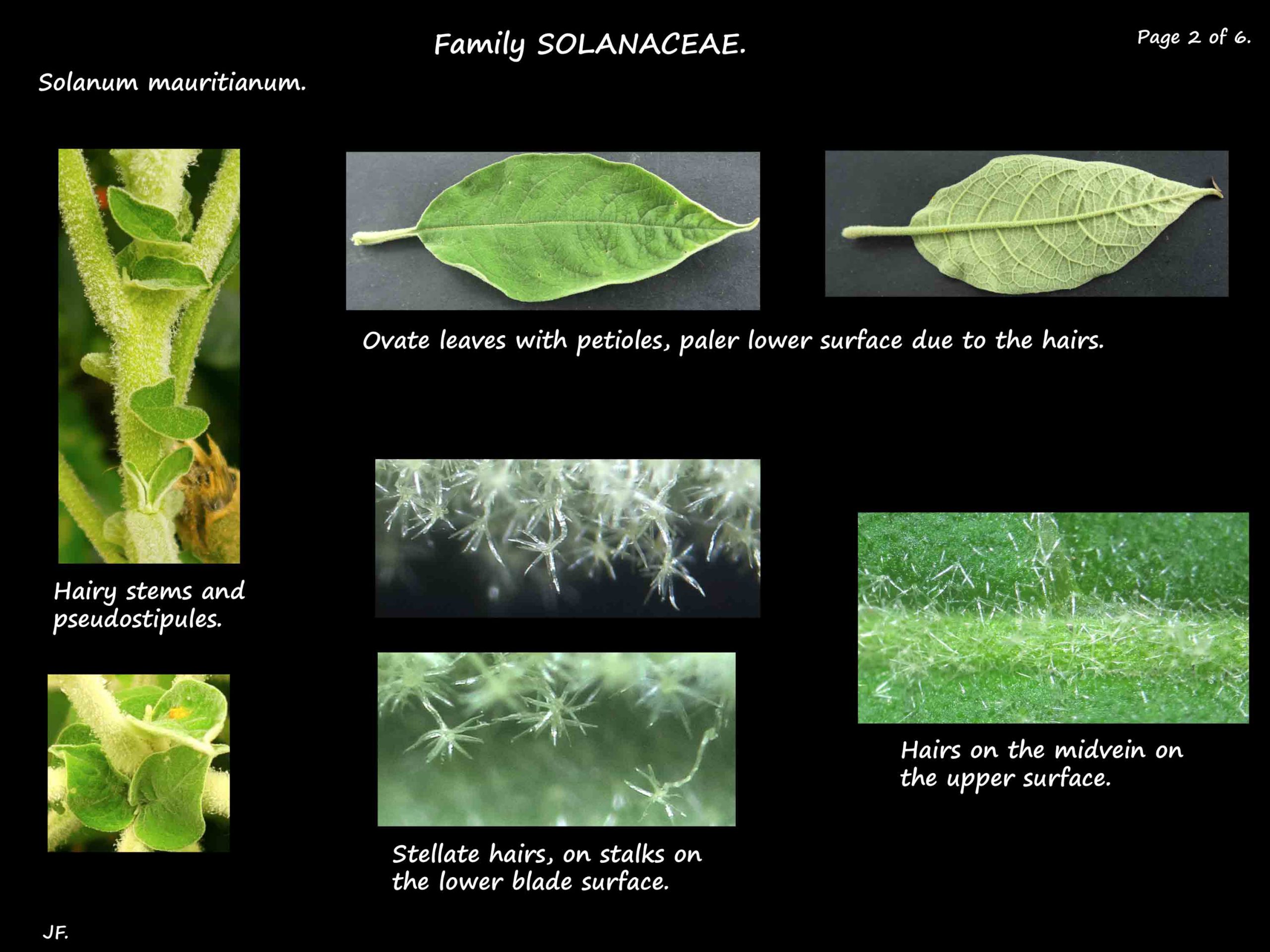
The alternate leaves are ovate to elliptic with a pointed tip and sometimes a wavy edge.
The hairy petioles are up to 5 cm long.
The blades are around 30 cm long and 4 to 12 cm wide.
The upper leaf surface is grey-green and the lower white to greyish.
This is due to the woolly, stellate hairs being much denser on the lower surface.
There are no prickles.
Apart from the small twigs there are 1 or 2 leafy pseudostipules in the leaf axils.
They are up to 2 cm long and have no stalk.
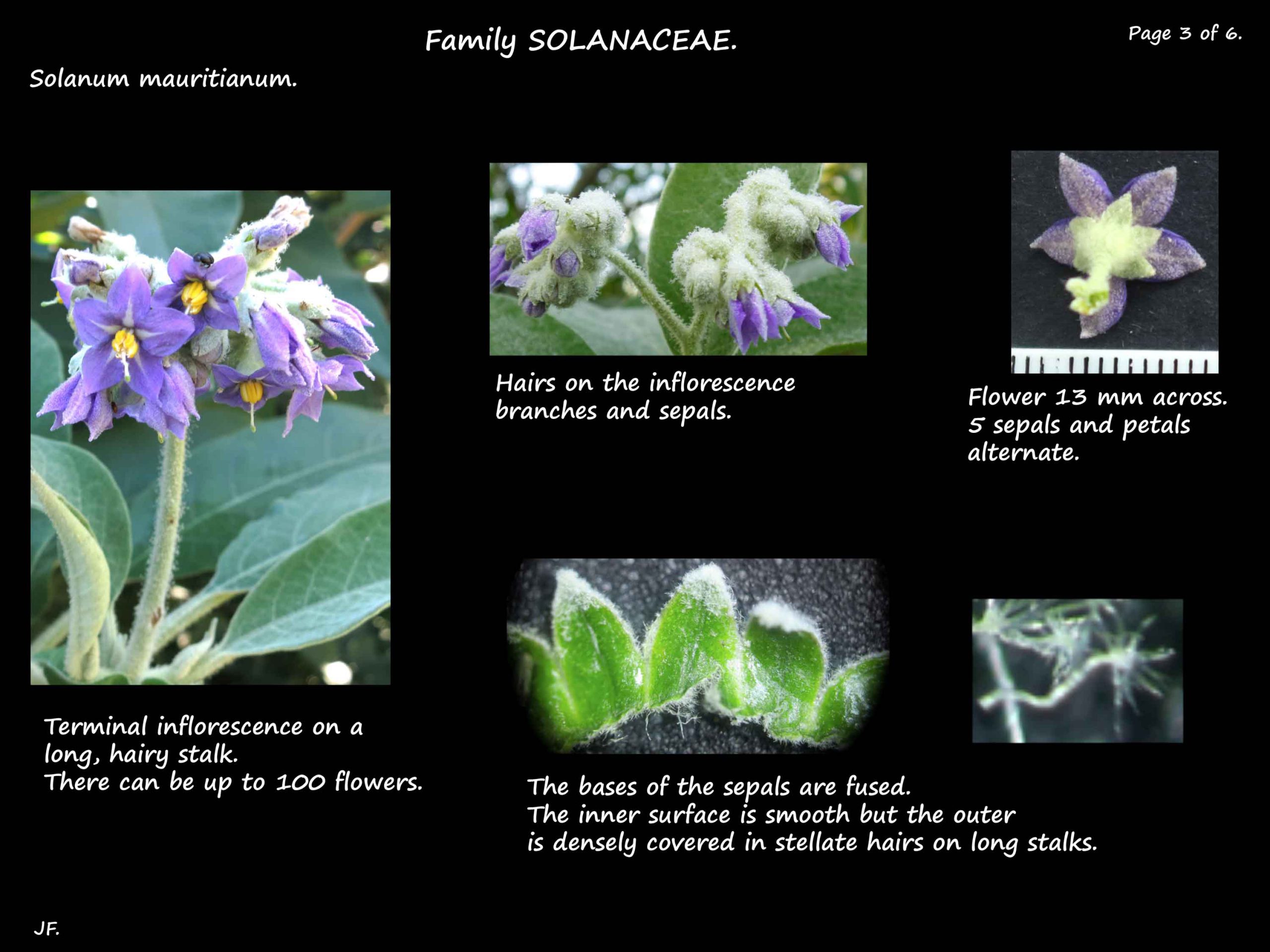
The branched terminal inflorescences can have up to 100 flowers.
The inflorescence stalk (peduncle) is around 16 cm long.
The individual flowers are on stalks (pedicels) 2 or 3 cm long.
The violet or purple flowers are around 2 cm across and have parts in 5’s.
The sepals are around 5 mm long with the bases fused into a short tube.
The triangular lobes are 2 to 3 mm long.
The outer surface is densely covered in stellate hairs.
The petals are around 15 mm long with the lower 2 to 3 mm fused into a tube.
The pointed lobes are purple to violet and have stellate hair on the outer surface.
There is often a white midrib on the lobes.
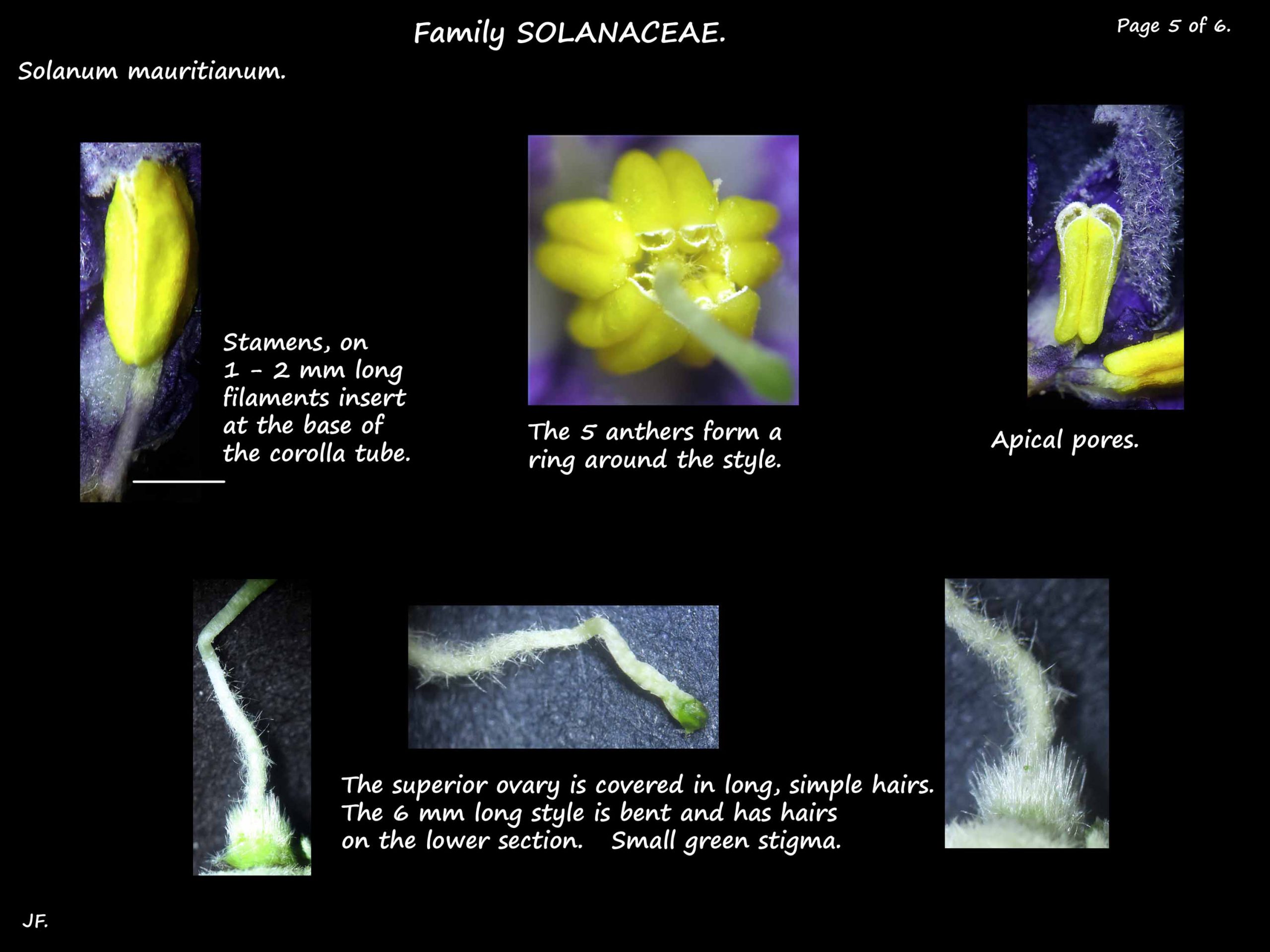
The stamens have 1 to 2 mm long filaments and anthers around 2.5 mm.
The tips of the anthers touch forming a ring around the style.
The superior ovary is densely hairy and the 6 mm style has a green stigma.
The fruit are spherical, green then pale yellow berries up to 1.5 cm across.
The calyx remains on the fruit.
Young fruit have dense stellate hairs but these are lost as the fruit grows.
Each fruit has many yellowish-brown seeds about 2 mm long.
J.F.