Pongamia pinnata.
Family Fabaceae s.s. (Family Fabaceae s.l. > Subfamily Faboideae).
World Flora Online (with Kew Science) has Pongamia as an accepted name and Millettia a synonym.
Synonyms include Millettia Pongamia, Pongamia glabra, Pongamia glabra var. minor and Pongamia pinnata var. typica.
Common names include pongamia and Wisteria tree.
It is native to India and S. E. Asia. The Queensland Herbarium considers it is also native to northern Queensland.
It is the only species in S. E. Queensland where it is naturalised in some areas.
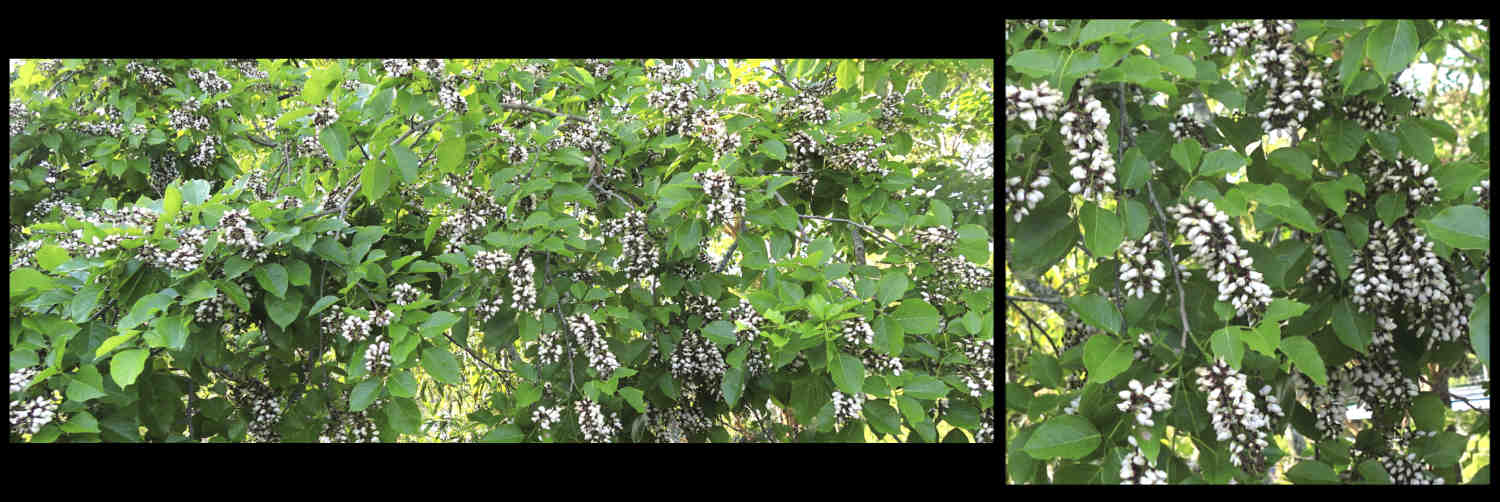
It is seen as a street tree and in parks.
Trees are usually around 10 to 15 m high but can grow to 25 m with a wide crown.
They have a large lateral root system and can produce suckers.
The bark on the trunk is grey to grey-brown and smooth to fissured.
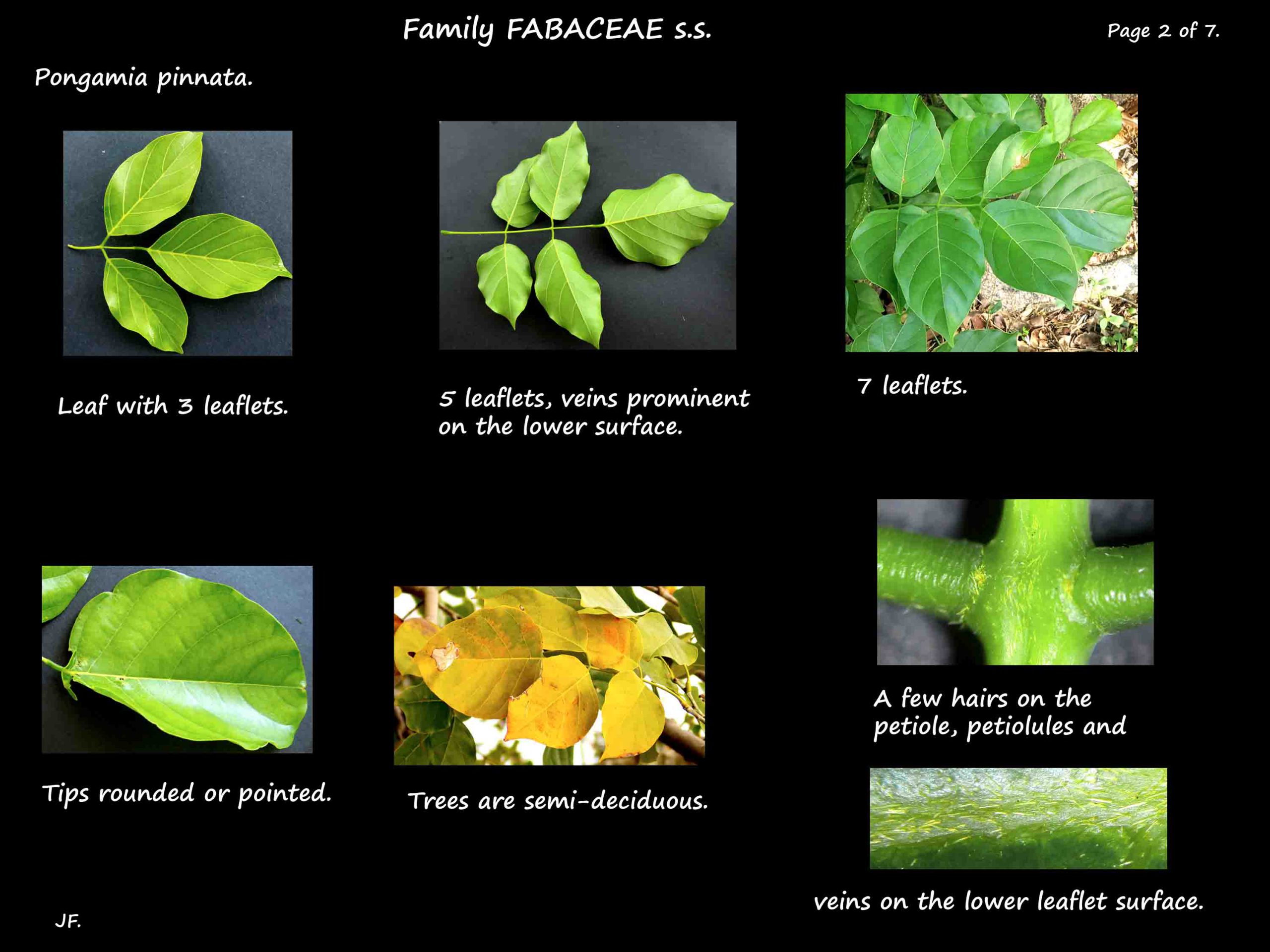
Alternately arranged leaves, including a petiole a few cms long, are up to 25 cm.
They are pinnate with mostly 5 or 7 leaflets but can have 3 or 9.
The upper surface of the petiole is grooved and there is a swelling at the base.
Leaflets, up to 10 cm long, are on stalks with the terminal stalk being the longest.
The blades are ovate, elliptic or oblong and the tip round to pointed.
New leaves are pinkish then they become a shiny, pale then dark green.
The veins are prominent on the lower surface.
Trees can be semi-deciduous with the leaves changing to yellow or reddish before they fall.
There are a few golden-brown hairs on the leaf parts.
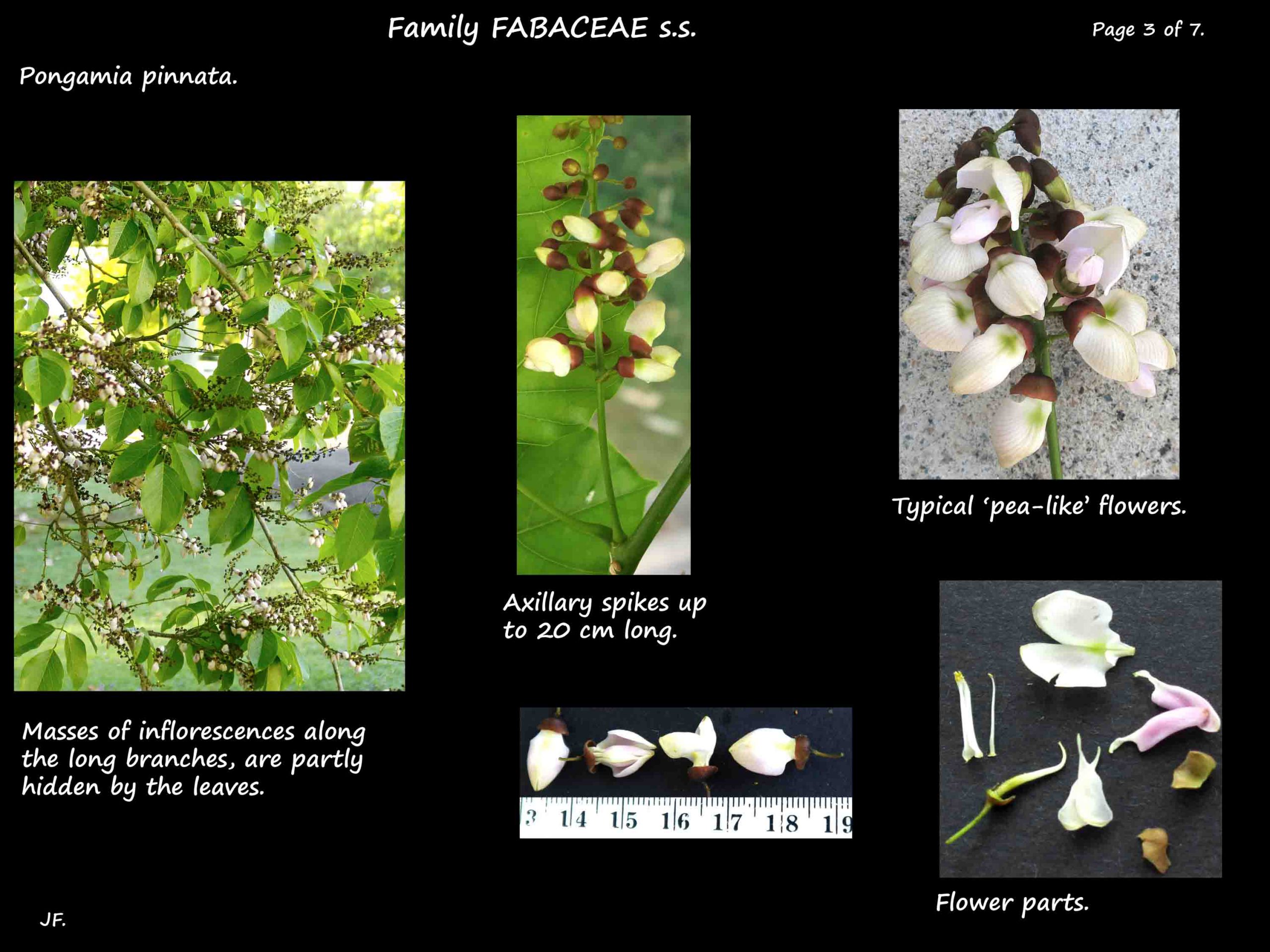
Axillary inflorescences are unbranched spikes seen along branches that are metres long.
The spikes are up to 20 cm long with new flowers continuing to open at the tip.
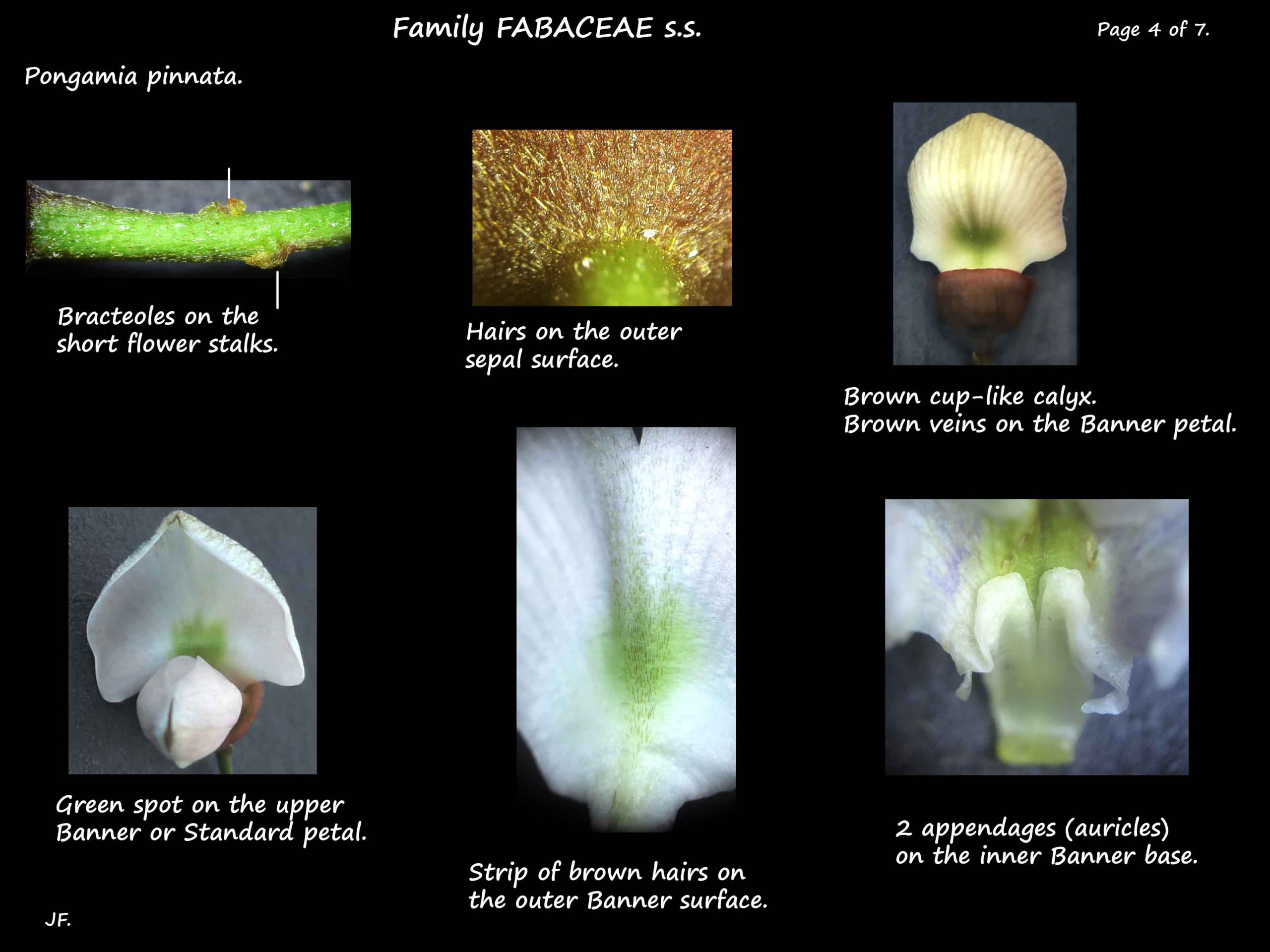
Each flower is on a short stalk with a pair of tiny bracteoles on it.
The pea-like flowers are around 1 cm long with parts in 5’s.
They are white with variable areas of pale pink to purple on some petals.
The calyx, of fused sepals, is cup-shaped with a flat rim or one with tiny teeth.
About 4 mm long, it is covered in short hairs externally.
The upper Standard or Banner petal is roughly circular with a claw base.
Just above the narrow base are 2 ear-like appendages that fold inwards.
It has a small greenish area above the narrow base and prominent brown veins.
There is a central strip of brown hairs on the outer or posterior surface.
The 2 wings, with narrow claw bases, are white to pale or a deeper pink or mauve.
They are around 1 cm long but only 3 mm wide and they hide the keel petals.
The 2 lower petals have their tips fused on the upper edge and are folded down to form the keel.
Each has a strip of brown hairs along the upper edge externally and to a lesser extent inside.
The keel hides most of the stamens and the ovary.
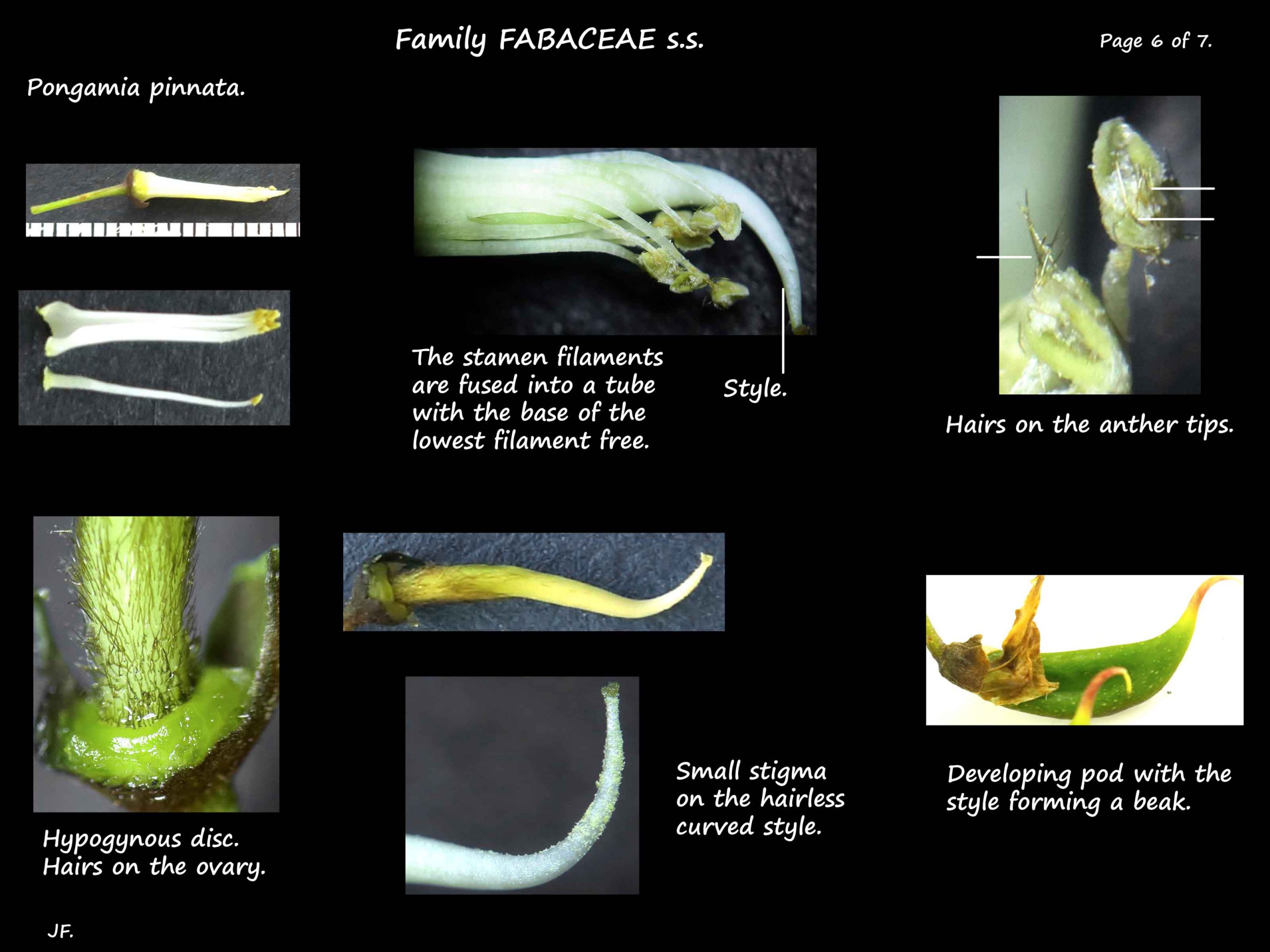
Nine of the 10 stamens have their filaments fused into a tube.
The lower part of the 10th stamen filament is free but then fuses with the others.
There are brown hairs growing from the connective tissue between the anthers.
There is a continuous nectiferous disc around the base of the ovary.
The flattened, hairy ovary is on a very short stalk.
The hairless style, which curves towards the end, has a small stigma.
The fruit are flattish oval pods up to 8 cm long and 3 cm wide.
They mature from green to grey and become hard and almost woody.
The style forms a short, curved beak at the end.
The pods decompose on the ground to release the 1 or 2 brown kidney-shaped seeds.
J.F.