Hibiscus.
Family Malvaceae > Subfamily Malvoideae > Tribe Hibisceae.
Figures for the number of species in the Mallow family vary from around 200 to 434 (Plants of the World Online)
or 571 World Flora Online. The wide range is due to genera or groups of species being moved around.
For example Hibiscus mutabilis has been known as Abelmoschus mutabilis and Ketmia mutabilis and Hibiscus cannabinus
as Abelmoschus congener, Furcaria cannabina, Ketmia glandulosa and Kosteletzkya vitifolia.
Around 35 species are native to Australia and some that were introduced as garden plants have become naturalised.
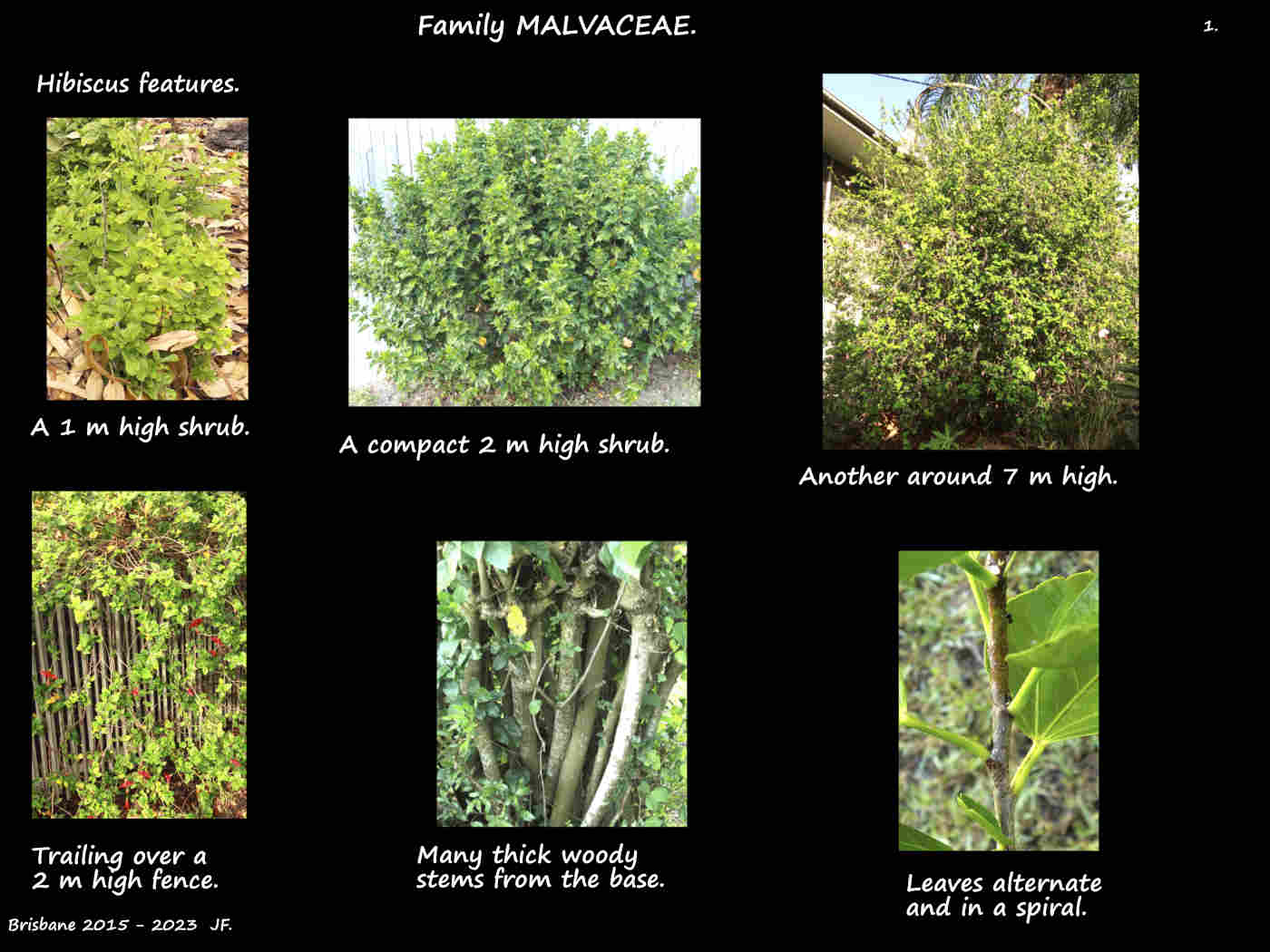
They can be annual herbs or woody perennial shrubs 1 to 2 m high or small trees over 6 m.
The green or red stems can be smooth or have white or rust coloured stellate hairs.
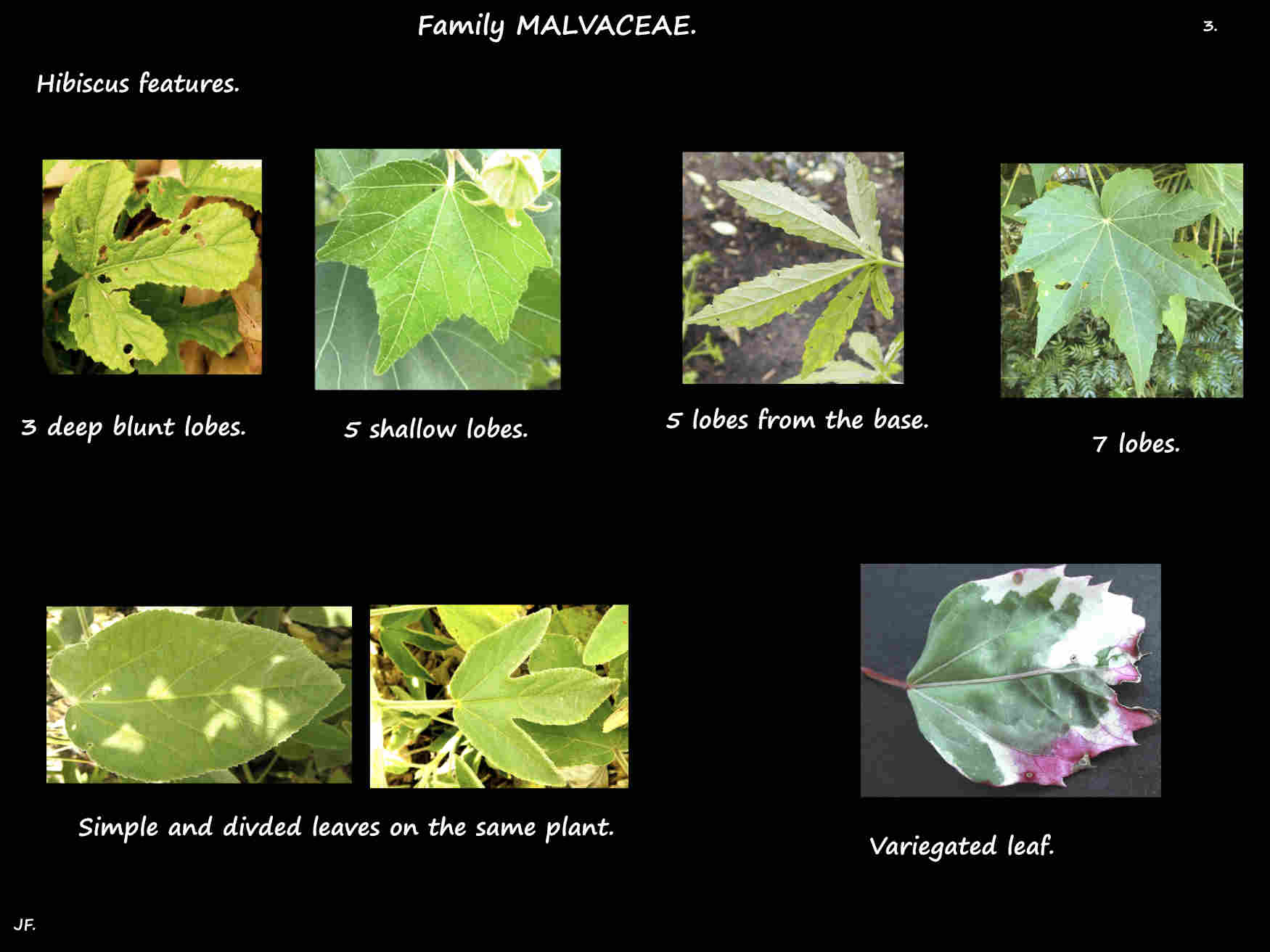
The alternately arranged ovate to lanceolate leaves are on petioles with linear or leafy stipules at the base.
The green or sometimes red blades can be up to 30 cm long and wide.
They may be entire or have 3 to 7 shallow to deep lobes.
There are often teeth and the edges may be wavy.
The lower surface may be smooth, have dense hairs or just a few on the veins.
The surfaces may be the same colour or the lower can be paler.
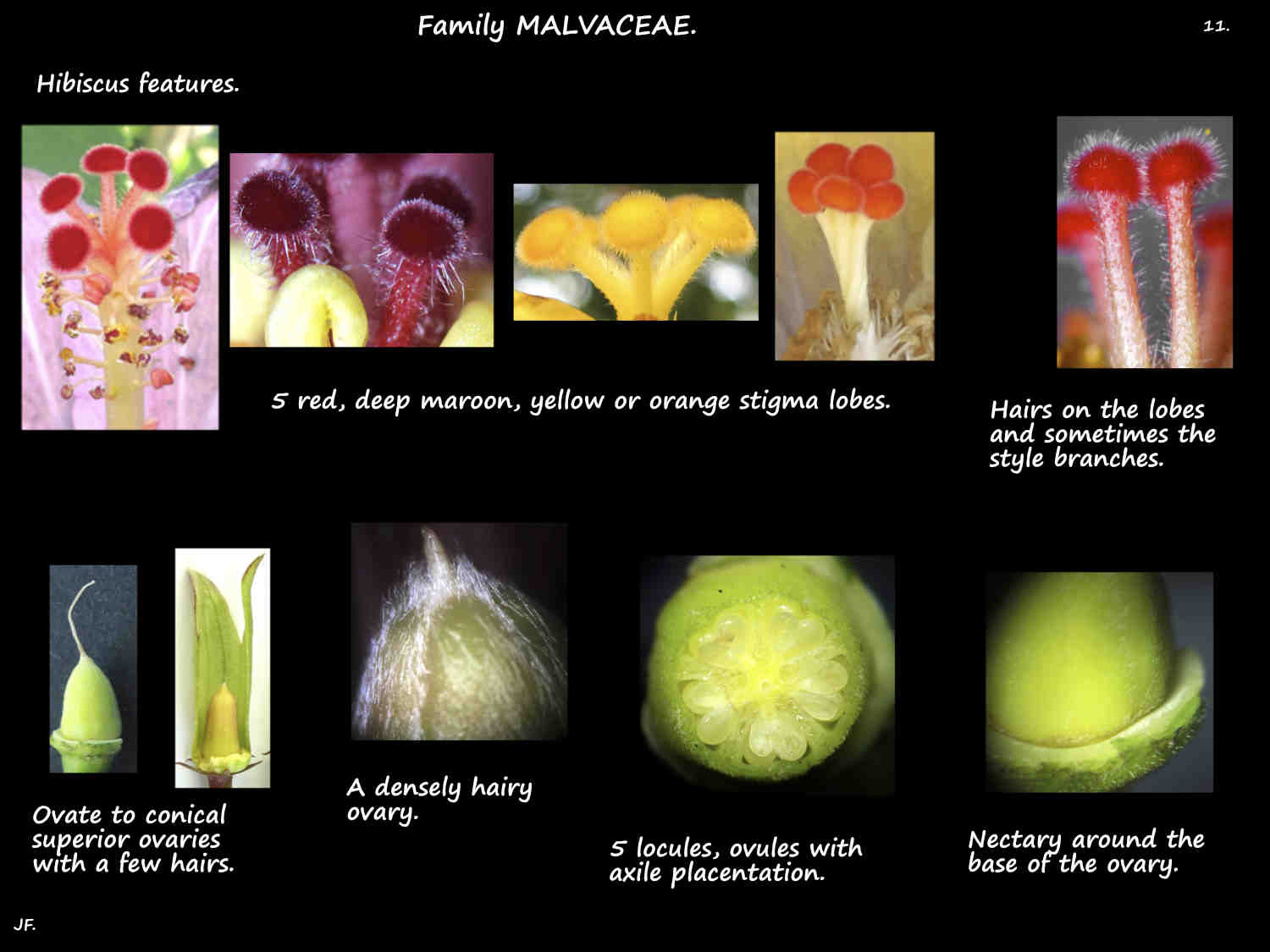
There may be a nectary on the lower midrib.
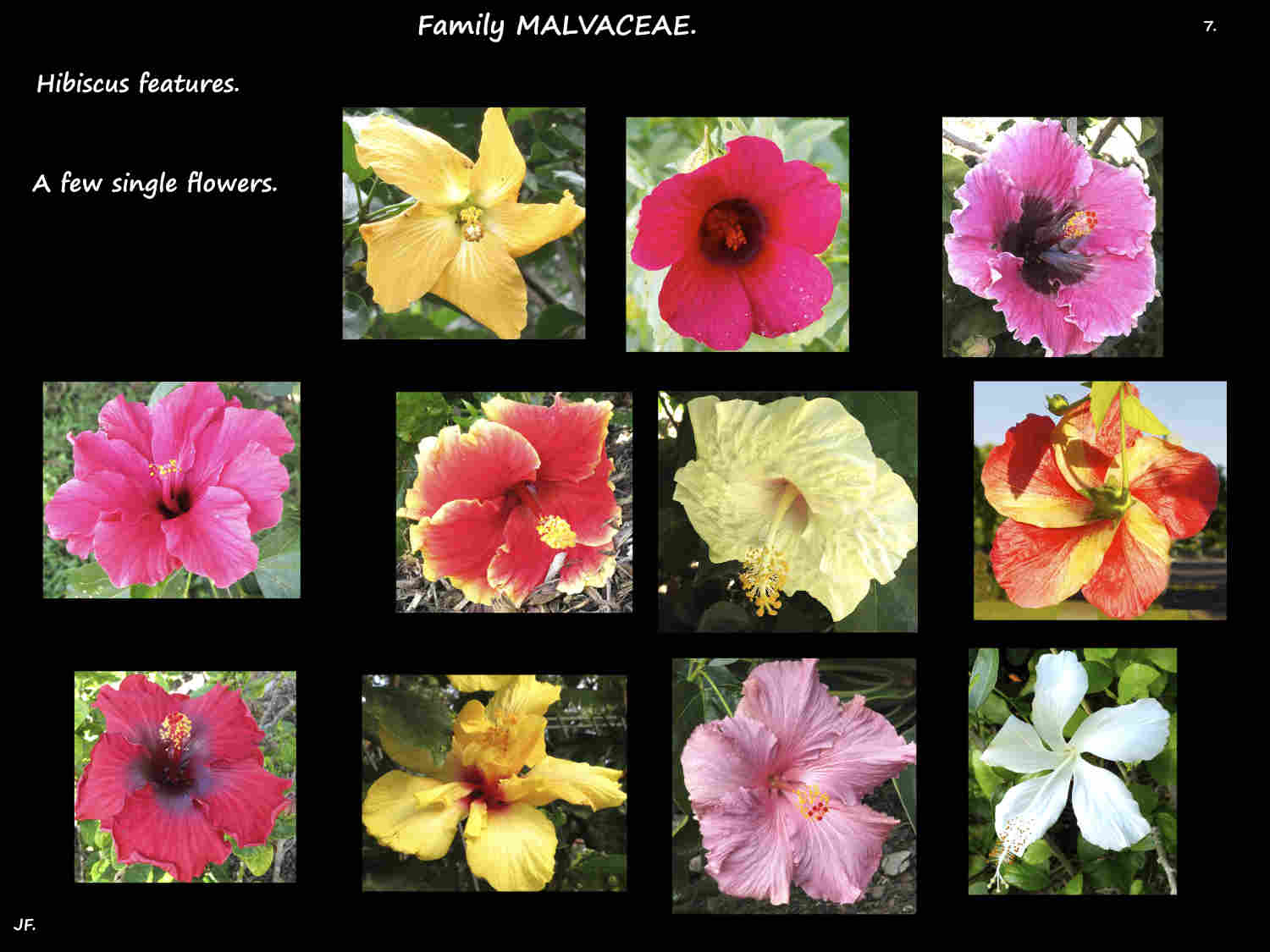
Inflorescences are mostly a solitary axillary flower that can be erect to pendulous.
The flowers are on a pedicel up to 20 cm long.
The free or fused bracts in the epicalyx can be up to 3 cm long.
There are simple or stellate hairs that can be dense or mostly near the edges.
The calyx has 5 sepals with glandular hairs and somtimes a nectary.
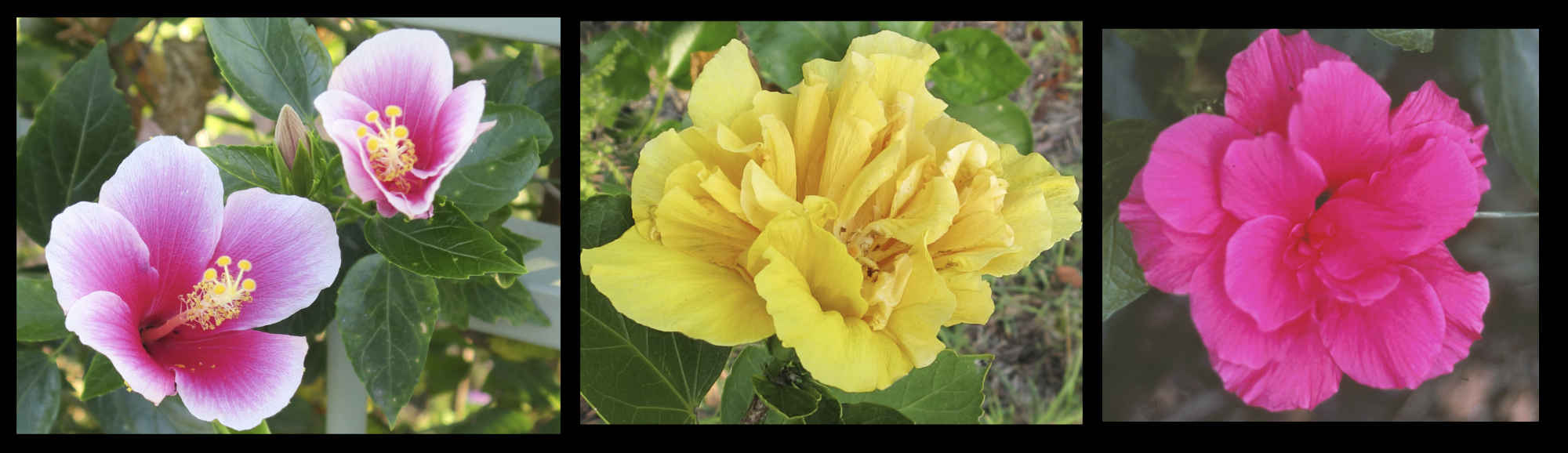
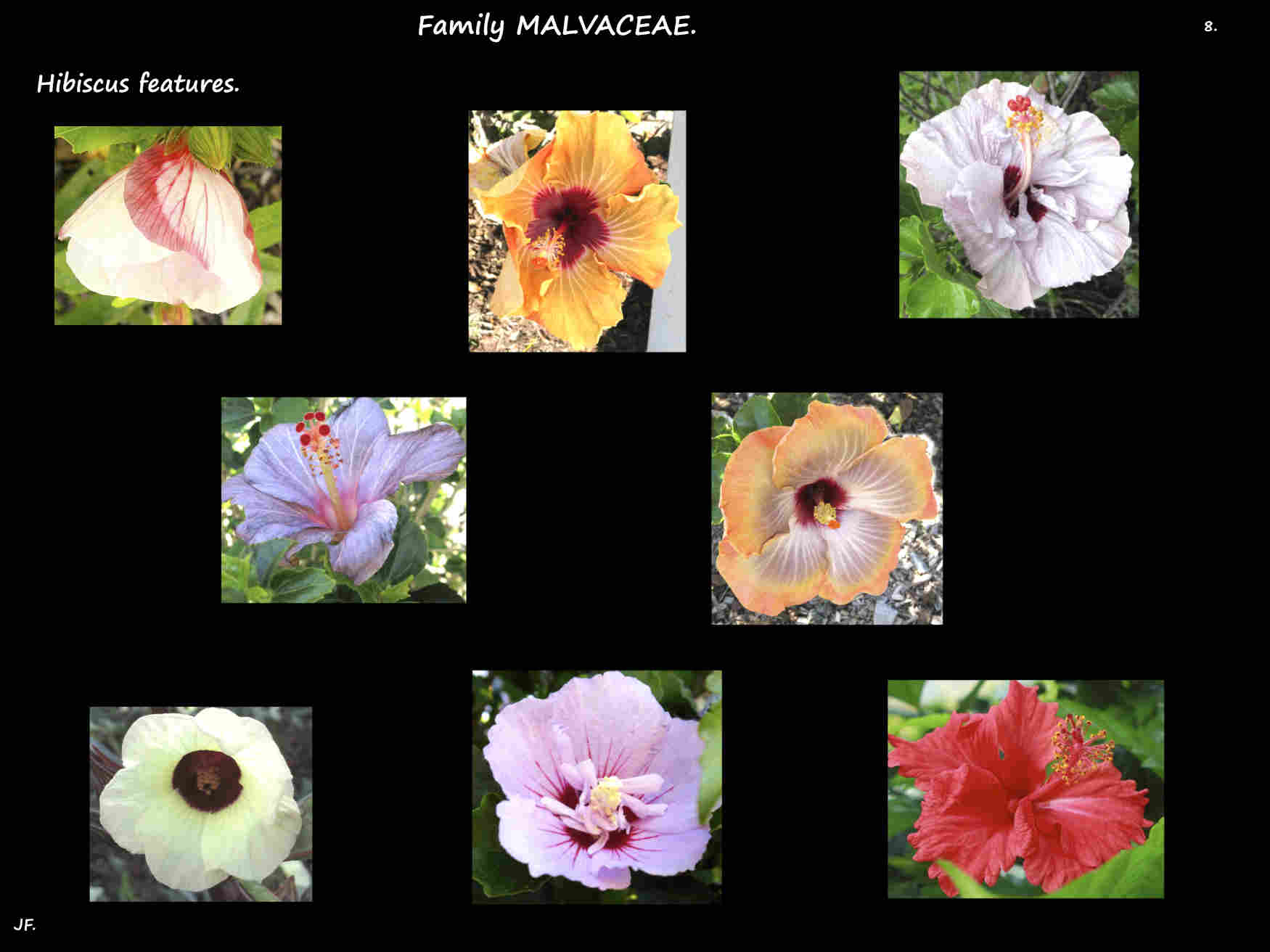
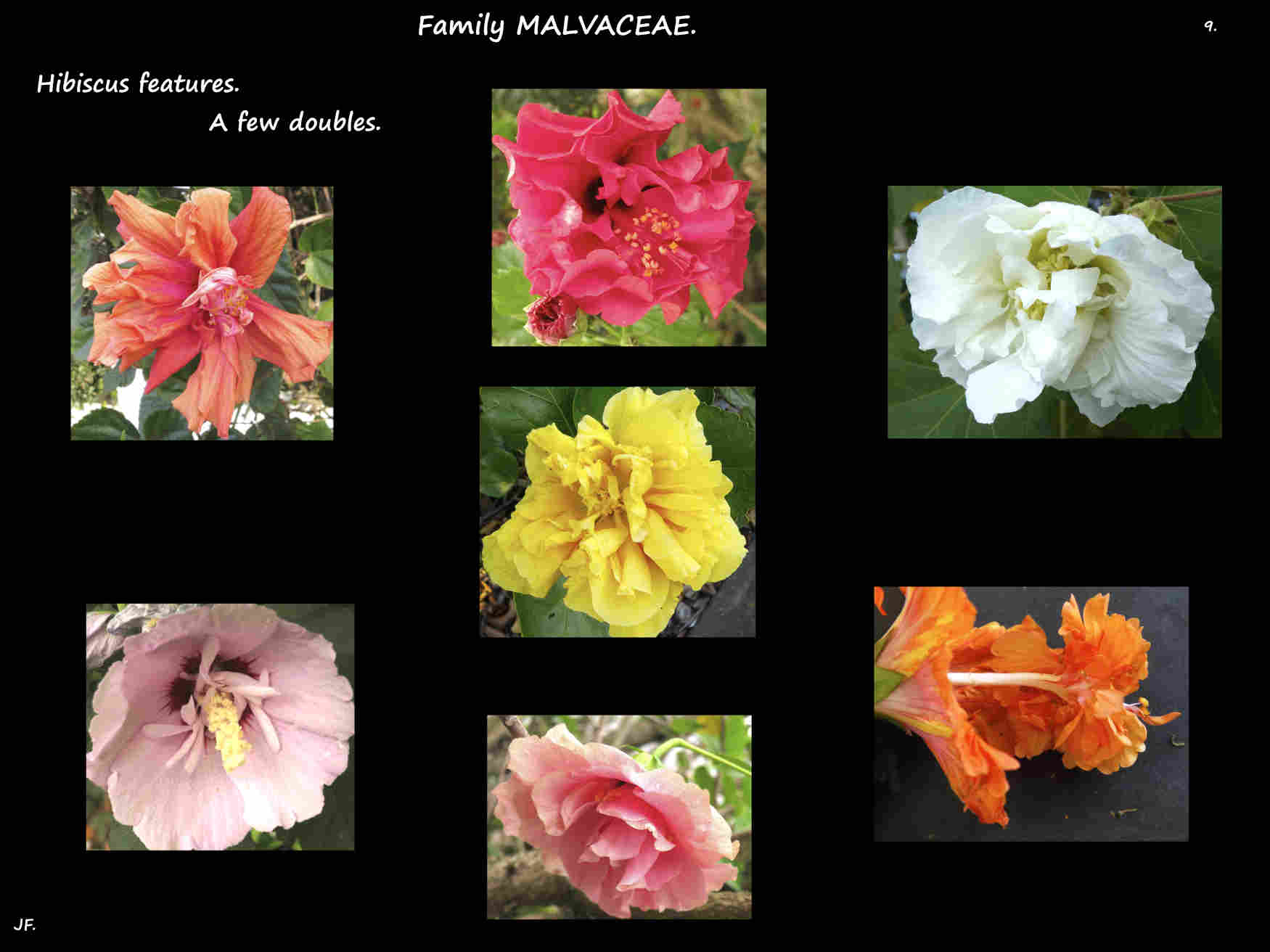
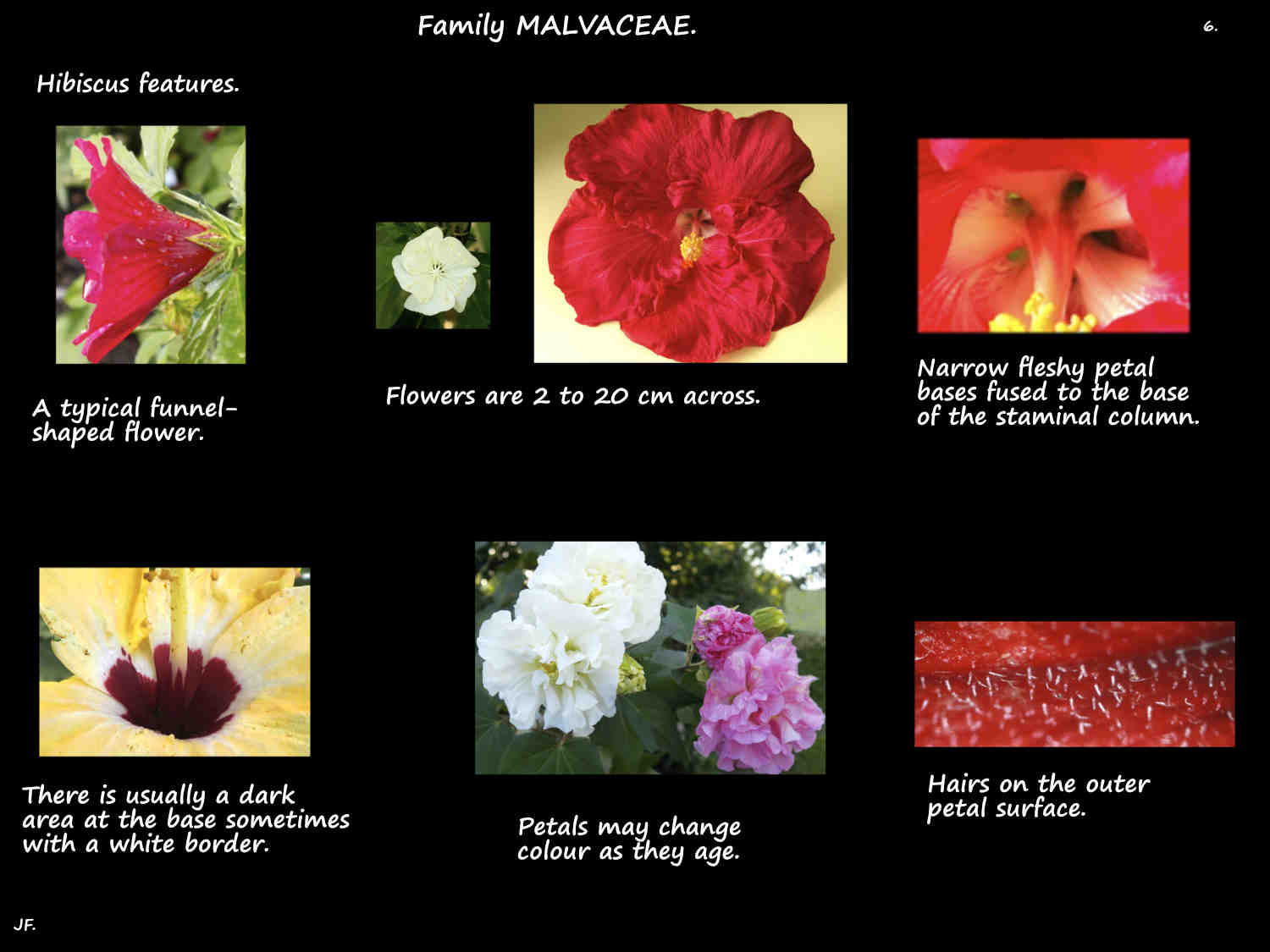
The trumpet-shaped corolla of 5 petals can be up to 14 cm long and 18 cm wide.
Petals may spread out or bend back and the edges may be fringed.
As well as white colours include pink, red, yellow orange, purple and bluish.
Some have a darker coloured spot at the base and some change colour as they age.
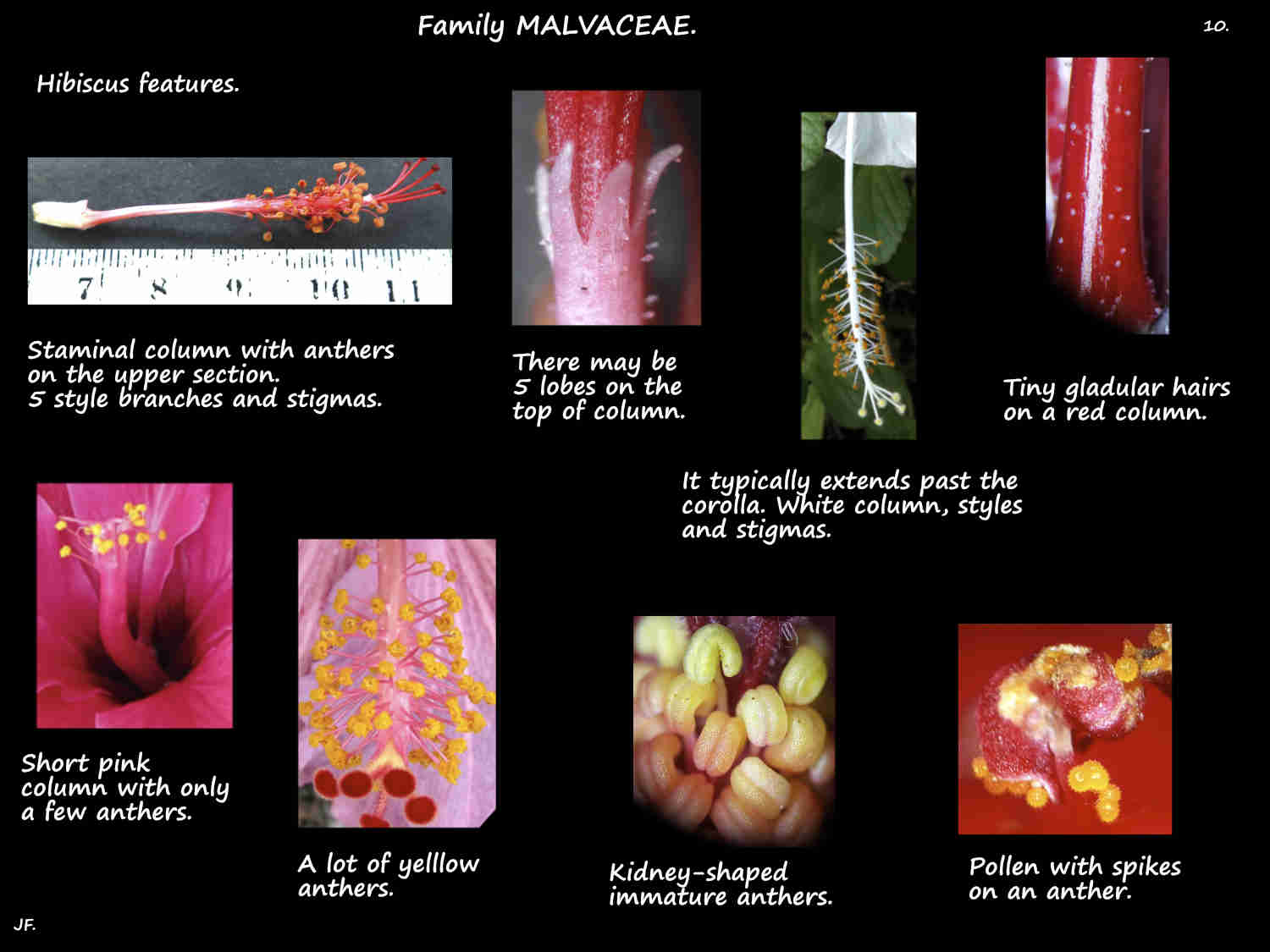
The stamen filaments are fused into a column with a flat top or one with 5 teeth.
The superior ovary has 5 locules with a few ovules in each.
The style runs up through the staminal column then splits into 5 branches.
Each spreading branch, up to around 5 mm long has a spherical (capitate) stigma.
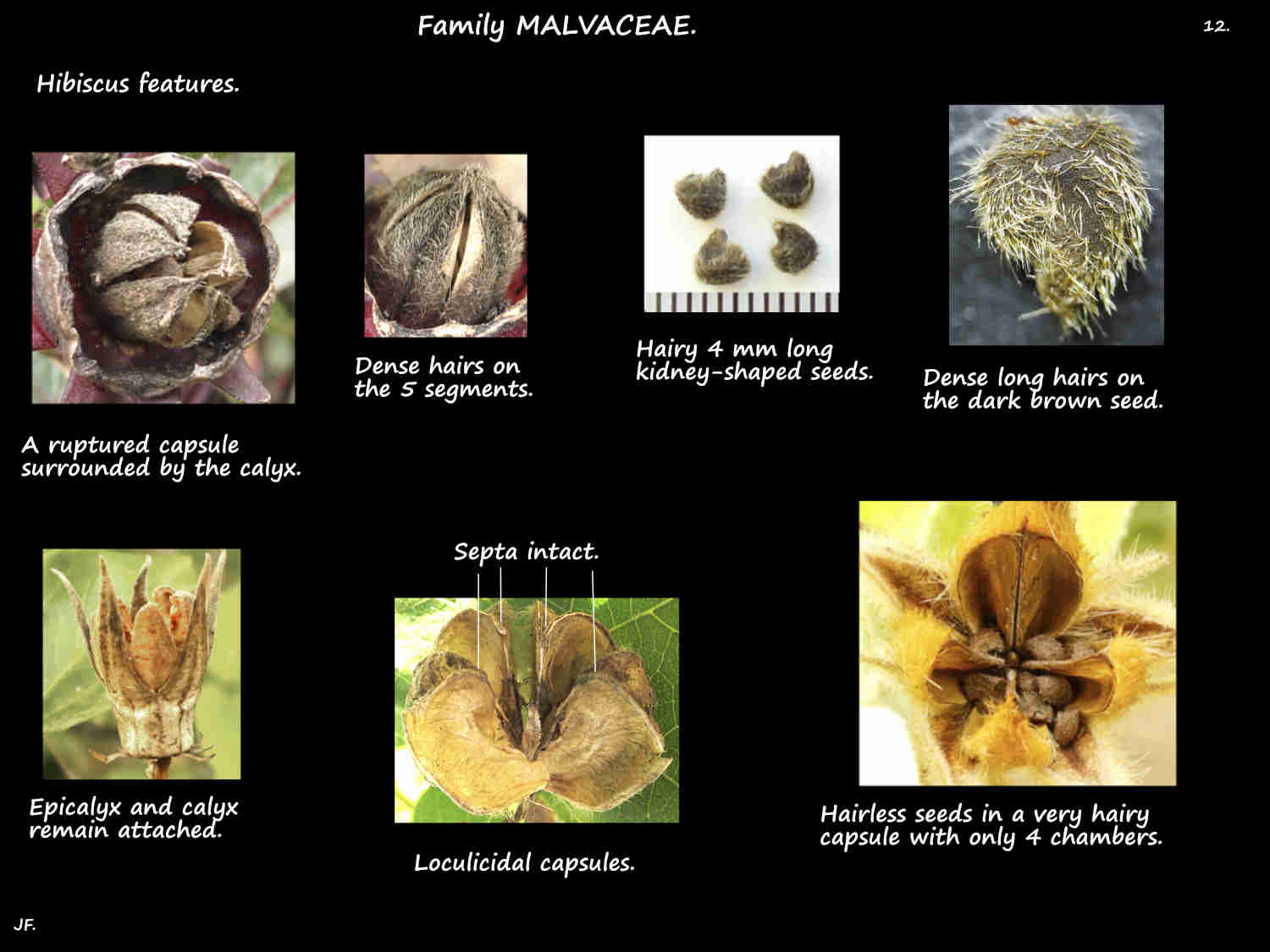
The fruit are loculicidal capsules up to 3.5 cm long that open into 5 valves or sections.
Capsules may be smooth, covered in dense hairs or just have a few on the sutures.
Each valve has several seeds, up to nearly 3 mm long that may be smooth or hairy.
J.F.